
Linux 之二:CentOS7 的 IP 常用命令和配置及 xshell 基本使用方法
输入 ipconfig (windows 查看ip的命令) 来查看真机的当前 IP。下面输入命令 ifconfig(注意:不是 ipconfig )或ip addr 来查看当前系统 IP。进入虚拟机,在命令终端 输入 ping 192.168.0.102 (我的真机的IP)点击右键---进入终端--输入 ip adrr 或 ifconfig 查看ip地址。win+R -- 打开 运行---输入 c
1. 进入虚拟机
点击右键---进入终端--输入 ip adrr 或 ifconfig 查看ip地址

下面输入命令 ifconfig(注意:不是 ipconfig ) 或 ip addr 来查看当前系统 IP

查看到IP 后,比如:上面是 192.168.184.137
1.1 IP 常用命令和配置
ifconfig 和 ip addr
ifconfig lo down : 卸载网卡 。 lo 是网卡名称, down 是命令
想查看所有网卡,使用命令
ifconfig -a
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig -a
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 ## UP 和 RUNNING 表示启用状态
inet 192.168.184.138 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.184.255
inet6 fe80::66a4:cbb9:7e27:e836 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:62:64:5d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 578379 bytes 825280501 (787.0 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 245312 bytes 14903334 (14.2 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=8<LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 ## 禁用 卸载的状态。
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
virbr0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.122.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.122.255
ether 52:54:00:3d:97:05 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
virbr0-nic: flags=4098<BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
ether 52:54:00:3d:97:05 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
再次启用网卡:
ifconfig lo up 启用 lo 网卡
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig lo up
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.184.138 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.184.255
inet6 fe80::66a4:cbb9:7e27:e836 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:62:64:5d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 579055 bytes 825335264 (787.1 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 245362 bytes 14910528 (14.2 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 ### 启用状态了
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
4.cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
5.traceroute 第一行就是自己的网关
6.ip route show
7.route -n
修改网络配置的文件:/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
静态IP
修改文件目录:/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
修改为静态:
- BOOTPROTO=static
指定IP、网关、子网掩码、域名解析器
IPADDR=192.168.75.100 GATEWAY=192.168.75.2 # 需要先查下网关,一般为最后一段为2 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 DNS1=114.114.114.114 DNS2=8.8.8.8
2. 进入真机CMD
win+R -- 打开 运行---输入 cmd----输入ipconfig

输入 ipconfig (windows 查看ip的命令) 来查看真机的当前 IP。注意:不是 ifconfig 是 ipconfig

3. 先测试 真机是否能访问 虚拟机
在真机的CMD 命令窗口中,输入 ping 192.168.184.137 回车
如果能出现下面的数据包响应,说明连通的

4. 测试虚拟机是否可以向外访问
进入虚拟机,在命令终端 输入 ping 192.168.0.102 (我的真机的IP)

注意:发测试数据包时,linux 中会一直发送,需要中断的话,可以使用 Ctrl+C 结束。
还可以测试外网是否连通
ping www.baidu.com
注意: window 查询IP :ipconfig
linux 查询IP : ifconfig 或 ip addr
5. 使用 xshell
如果上面的步骤通过,确定可以由外向内访问的话,我们就可以使用客户端 xshell 来操作linux 了
1)打开 Xshell 界面
上面菜单图标中,有三个常用的连接管理。

2)新建连接
点击第一个图标 加号的图标

3)编辑登录信息
上面输入IP后,下面配置登录信息

4)保存连接信息
完成后,点击确定即可。
下面开始连接: 点击左边菜单列表中的连接名.
再选择接受和保存

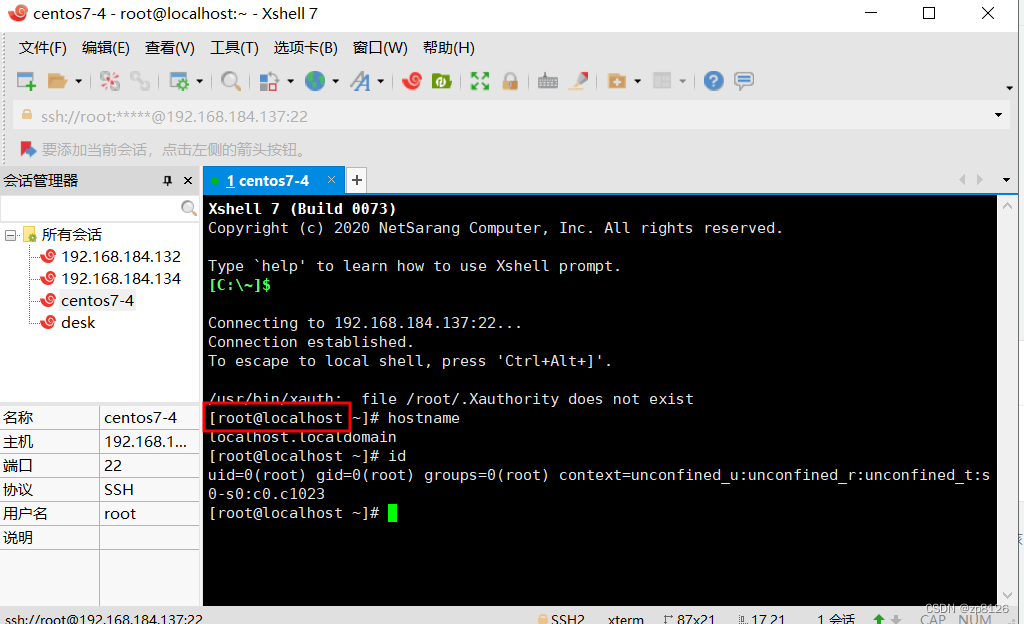
5)进入shell 窗口
进入shell 窗口后,就可以正常使用 linux 的命令,来通过客户端远程操作 linux 服务器了
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容









所有评论(0)