Netty之BIO(同步阻塞IO)、PIO(伪异步阻塞IO)、NIO(异步非阻塞IO)、AIO(异步非阻塞IO)、Netty
学习书籍:Netty权威指南多种IO方式的比较:1、BIO(同步阻塞IO)使用ServerSocket绑定IP地址和监听端口,客户端发起连接,通过三次握手建立连接,用socket来进行通信,通过输入输出流的方式来进行同步阻塞的通信每次客户端发起连接请求,都会启动一个线程线程数量:客户端并发访问数为1:1,由于线程是JAVA虚拟机中非常宝贵的资源,一旦线程数急剧增加,系统性能会急
学习书籍:Netty权威指南
多种IO方式的比较:
1、BIO(同步阻塞IO)
使用ServerSocket绑定IP地址和监听端口,客户端发起连接,通过三次握手建立连接,用socket来进行通信,通过输入输出流的方式来进行同步阻塞的通信
每次客户端发起连接请求,都会启动一个线程
线程数量:客户端并发访问数为1:1,由于线程是JAVA虚拟机中非常宝贵的资源,一旦线程数急剧增加,系统性能会急剧下降,导致线程栈溢出,创建新的线程失败,并最终导致宕机
所以在JDK1.4之前,人们想到了一种方法,即PIO方式
2、PIO(伪异步阻塞IO)
使用线程池来处理客户端的请求
客户端个数:线程池最大线程数=M:N,其中M远大于N
在read和write的时候,还是IO阻塞的,只是把每个线程交由线程池来控制管理
3、NIO(异步阻塞IO)
用NIO方式处理IO
使用多路复用器Selector来轮询每个通道Channel,当通道中有事件时就通知处理,不会阻塞
使用相当复杂
4、AIO(真正的异步非阻塞IO)
NIO2.0引入了新的异步通道的概念,不需要使用多路复用器(Selector)对注册通道进行轮询即可实现异步读写,从而简化了NIO编程模型
使用Netty框架进行编程步骤
1、构建事件处理池
2、使用引导程序关联事件处理池、通道、事件处理器
3、绑定端口服务
4、等待操作完成
5、关闭事件处理池
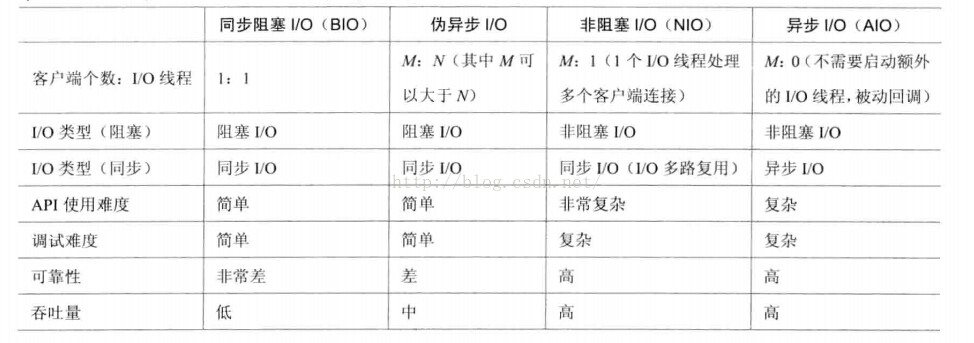
几种IO的功能和特性对比
按照书上的例子码了一遍:
服务端:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class NettyServer {
public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
// 等待服务端监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandle());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
new NettyServer().bind(port);
}
}
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
public class NettyServerHandle extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("The time server receive order:" + body);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.write(resp);
}
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}客户端:
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class NettyClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) throws Exception {
// 1、创建线程池
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 2、使用引导器关联线程池、通道、通达处理器、设置执行参数
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandle());
}
});
// 发起异步连接操作 3、绑定端口同步操作
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
// 4、监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放NIO线程组 5、释放资源
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
new NettyClient().connect(port, "127.0.0.1");
}
}客户端处理器:
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class NettyClientHandle extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger
.getLogger(NettyClientHandle.class.getName());
private final ByteBuf firstMessage;
public NettyClientHandle() {
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();
firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
firstMessage.writeBytes(req);
}
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);
}
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("Now is:" + body);
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// 释放资源
logger.warning("Unexpected exception from downstream:"
+ cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)