HTML四种常见的定位-相对定位
HTML四种常见的定位-相对定位
·
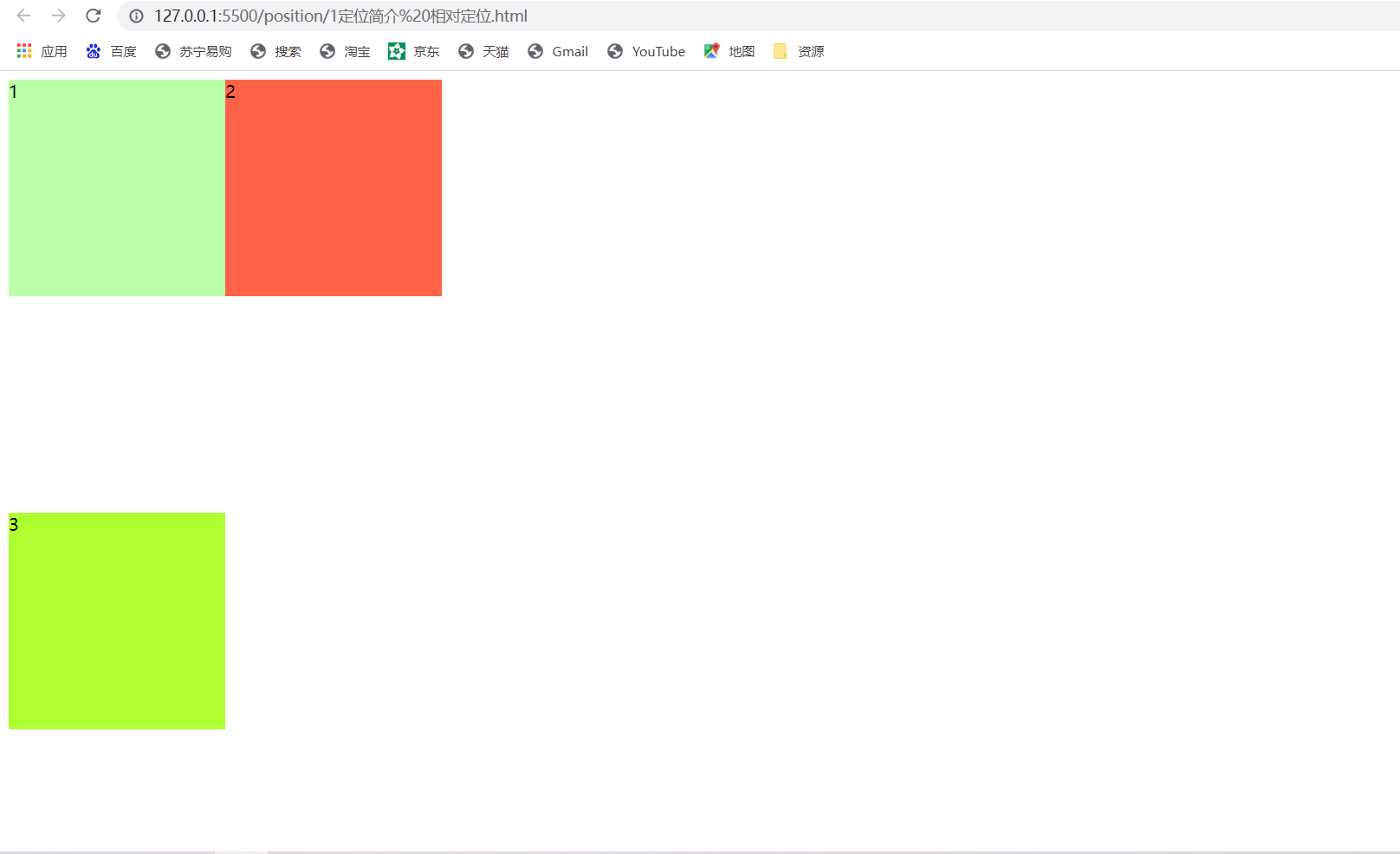
相对定位 1 <!DOCTYPE html>
2 <html lang="en">
3 <head>
4 <meta charset="UTF-8">
5 <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
6 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
7 <title>Document</title>
8 <style>
9 .box1{
10 width: 200px;
11 height: 200px;
12 background-color: #bfa;
13
14 }
15 .box2{
16 width: 200px;
17 height: 200px;
18 background-color: tomato;
19 /* 定位(position)
20 -定位是一种更加高级的布局手段
21 -通过定位我们可以将元素摆放在页面的任意位置
22 -使用position设置定位
23 可选值:
24 satatic 默认值 :元素是静止的 没有开启定位
25 relative 相对定位
26 absolute 绝对定位
27 fixed 固定定位
28 sticky 粘滞定位
29 -相对定位(相对定位是相对于其本身原来的位置进行定位)
30 -当元素的position设置为relative
31 -相对定位的特点:
32 1、开启相对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何变化
33 2、相对定位是参照元素在文档流中的位置进行定位的
34 3、相对定位会提升元素的层级
35 4、相对定位不会使元素脱离文档流
36 6、相对定位不会改变元素的性质,块还是块,行内还是行内
37 偏移量(offset)
38 -当元素开启了定位以后,可以通过偏移量来设置元素的位置
39 top
40 -定位元素和定位位置上边的距离
41 bottom
42 -定位元素和定位位置下边的距离
43
44 -定位元素垂直方向的位置由top和bottom两个属性来控制
45 通常情况下我们只会使用其中之一
46 -top值越大,定位元素越向下移动
47 -bottom值越大,定位元素越向上移动
48 left
49 -定位元素和定位位置左侧的距离
50 right
51 -定位元素和定位位置右侧的距离
52
53 -定位元素水平方向的位置由left和right两个属性确定
54 通常情况下只会使用一个
55 -left越大元素越靠右
56 -right越大元素越靠左
57 */
58 position: relative;
59 left: 200px;
60 top: -200px;
61
62 }
63 .box3{
64 width: 200px;
65 height: 200px;
66 background-color: greenyellow;
67
68 }
69 </style>
70 </head>
71 <body>
72 <div class="box1">1</div>
73 <div class="box2">2</div>
74 <div class="box3">3</div>
75 </body>
76 </html>相对定位是相对于元素本身的原始位置进行定位相对定位是相对于元素本身的原始位置进行定位

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献20条内容
已为社区贡献20条内容









所有评论(0)