K8S 安全认证
1. 安全机制1.1 认证 (Authentication)1.1.1 认证方式HTTP Token:Authorization: Bearer $TOKENHTTP Basic: Authorization: Basic $(base64encode USERNAME:PASSWORD),HTTPS: 基于CA根证书签名的客户端身份认证方式(推荐)证书颁发:手动签发:通过k8s集群的根 ca 进
1. 安全机制
1.1 认证 (Authentication)
1.1.1 认证方式
-
HTTP Token:
Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN -
HTTP Basic:
Authorization: Basic $(base64encode USERNAME:PASSWORD), -
HTTPS: 基于CA根证书签名的客户端身份认证方式(推荐)
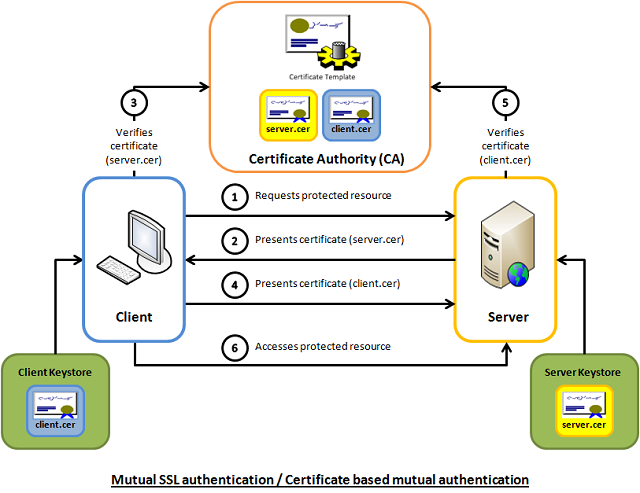
证书颁发:
- 手动签发:通过k8s集群的根 ca 进行签发 HTTPS 证书
- 自动签发:kubelet 首次访问 API Server 时,使用 token 认证通过后,Controller Manager 会为kubelet生成一个证书,以后的访问均使用该证书
1.1.2 认证方案
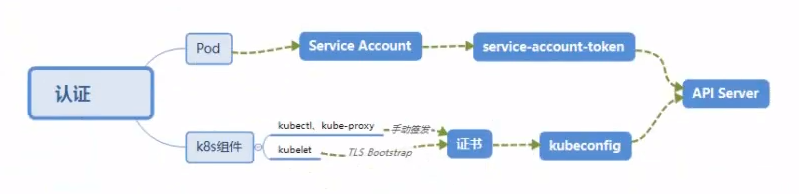
-
kubeconfig
kubeconfig 文件包含集群参数(CA证书、API Server地址),客户端参数,集群context信息(集群名称、用户名)。k8s 组件通过启动时指定不同的 kubeconfig 文件可以切换到不同的集群
cat ~/.kube/config -
ServiceAccount
Pod 中的容器访问API Server。因为Pod的创建和销毁是动态的,所以要为它手动生成证书是不可行的,k8s 使用 Service Account解决Pod访问API Server的认证问题
1.2 鉴权 (Authorization)
API Server的授权策略,通过启动参数--authorization-mode
-
AlwaysDeny: 拒绝所有请求,一般用于测试
-
AlwaysAllow: 接收所有请求。如果集群不需要授权流程,采用该策略
-
ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control): 基于属性的访问控制,表示使用用户配置的授权规则对用户请求进行匹配和控制
-
Webbook: 通过调用外部REST服务对用户进行授权
-
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control): 基于角色的访问控制,默认规则,其优点如下
-
对集群中的资源和非资源均拥有完整的覆盖
-
整个RBAC完全由几个API对象完成,同其他API对象一样,可以用kubectl或API进行操作
-
可在运行时调整,无需重启API Server
-
1.3 准入控制
准入控制是 API Server 的插件集合,通过添加不同的插件,实现额外的准入控制规则
常见准入控制插件:
- NamespaceLifecycle: 防止在不存在的namespace上创建对象;防止删除系统预置的namespace;删除namespace时,连带删除它下面的所有资源
- LimitRanger: 确保请求的资源不会超过资源所在Namespace的LimitRange的限制
- ServiceAccount: 实现自动化添加SA
- ResourceQuota: 确保请求的资源不会超过资源的ResourceQuota限制
1.4 总结
API Server 是集群内部各个组件通讯的中介,也是外部控制的入口。k8s 使用认证(Authentication)、鉴权(Authorization)、准入控制(Admission Control) 三步来确保API Server的安全。
认证 和鉴权:
- 认证(authencation): 通过只代表通讯双方是可信的
- 鉴权(authorization): 确定请求方有哪些资源权限
2. ServiceAccount
2.1 kubernetes 账户
-
UserAccount:给集群外用户访问 API Server,执行 kubectl 命令时用的就是该账号。它是全局性的,跨 namespace, 通常为admin,也可以自定义
$ cat /root/.kube/config users: - name: cluster-admin user: -
ServiceAccount:Pod 容器访问 API Server 的身份认证。它与 namespace 绑定,每个namespace 都会自动创建一个默认的 SA。创建 Pod 时,如果未指定 SA, 则使用默认的SA,可通过配置
spec.serviceAccount指定 SA# default namespace SA $ kubectl get sa default -o yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: default namespace: default secrets: - name: default-token-gqgrp
2.2 什么是 SA
SA 是一种特殊的 secret,类型为 kubernetes.io/service-account-token,它由三部分组成:
- token:由 API Server 私钥签发的 JWT,Pod访问API Server的凭证
- ca.crt:根证书,用于Client端验证API Server发送的证书,与 /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.pem 一致
- namespace:该service-account-token的作用域名空间,Pod 所属 namespace
$ kubectl run -it nginx --rm --image=nginx -- /bin/bash
root@nginx:/# ls /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
ca.crt namespace token
2.3 自定义 SA
$ kubectl create ns my-ns
$ kubectl create sa my-sa -n my-ns
$ kubectl get sa -n my-ns
NAME SECRETS AGE
default 1 18s
my-sa 1 12s
$ kubectl get secret -n my-ns
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
default-token-xp4hg kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 42s
my-sa-token-xs257 kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 36s
Pod 中SA 配置:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-sa
namespace: my-ns
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
serviceAccountName: my-sa # 指定 SA
3. RBAC
3.1 概述
ServiceAccount 是 APIServer 的认证过程,而授权机制通过 RBAC:基于角色的访问控制实现(Role-based access control )
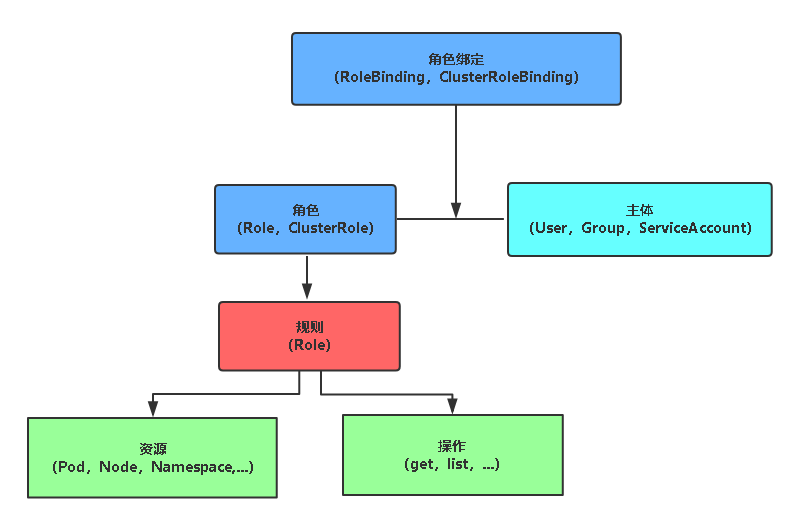
kubernetes 中所有资源对象都是模块化的 API 对象,允许执行 CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) 操作:
-
资源:pods,configmaps,deployments,nodes,secrets,namespaces,services 等
-
动作:create,get,delete,list,update,edit,watch,exec,patch
API 对象在 Etcd 里的完整资源路径,由三部分组成:
- Group:
/apis/batch - Version:
v1 - Resource:
cronjobs
# APIs
$ kubectl get --raw /
{
"paths": [
"/api",
"/api/v1",
"/apis",
"/apis/",
......
"/version"
]
}
# API 详情
kubectl get --raw /apis/batch/v1 | python3 -m json.tool
{
"kind": "APIResourceList",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"groupVersion": "batch/v1",
"resources": [
{
"name": "cronjobs",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "CronJob",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"cj"
],
"categories": [
"all"
],
"storageVersionHash": "h/JlFAZkyyY="
},
...
}
3.2 Role & ClusterRole
Role:表示一组规则权限,权限只会增加(累加权限),它定义的规则,只适用于单个 namespace
ClusterRole:集群级别的权限控制
- 集群级别资源控制,如 node 访问控制
- 非资源型 endpoints,如对某个目录和文件的访问:/healthz
- 所有命名空间资源控制 (Pod、Deployment等)
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: my-role
namespace: my-ns
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # 默认 core api group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get","list","create","update","patch","delete","watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: my-clusterrole
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
verbs: ["get","create","list"]
系统默认的 ClusterRole: cluster-admin,具有所有资源的管理权限
$ kubectl get clusterrole cluster-admin -o yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: cluster-admin
rules:
- apiGroups:
- '*'
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- nonResourceURLs:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
3.3 Subject
尝试访问和操作 API Server 的对象:
UserAccount:集群外的用户账号Group:用户组,集群中有一些默认创建的组,比如 cluster-adminServiceAccount:集群内的服务账号,它和 namespace 进行关联,适用于集群内部运行的应用程序,需要通过 API 来完成权限认证,所以在集群内部进行权限操作,我们都需要使用到 ServiceAccount
3.4 RoleBinding & ClusterRoleBinding
RoleBinding:将 Role 或 ClusterRole 授权给 Subject,它与 namespace 绑定
ClusterRoleBinding:将 ClusterRole 授权给 Subject,属于集群范围内的授权,与 namespace 无关
# 绑定 Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: my-rolebinding-1
namespace: my-ns
subjects:
- kind: User # 权限资源类型
name: eli # 名称
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: my-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
# 绑定 ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: my-rolebinding-2
namespace: my-ns
subjects:
- kind: User
name: eli
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: my-clusterrole
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: my-clusterrolebinding
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: developer
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: my-clusterrole
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
3.5 示例
3.5.1 UserAccount (namespace)
- user: eli
- organization:exped.top
- 创建用户凭证
# 创建私钥
openssl genrsa -out eli.key 2048
# 创建证书请求文件
openssl req -new -key eli.key -out eli.csr -subj "/CN=eli/O=exped.top"
# 使用CA证书签发证书
openssl x509 -req -in eli.csr -CA /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt -CAkey /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.key -CAcreateserial -out eli.crt -days 365
# 在集群中创建用户凭证
kubectl config set-credentials eli --client-certificate=eli.crt --client-key=eli.key
# 创建上下文
kubectl config set-context eli-context --cluster=kubernetes --namespace=kube-system --user=eli
# 暂未给用户赋予任何权限,无法进行操作
kubectl get pods --context=eli-context
Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidd
- 创建角色并绑定
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: eli-role
namespace: kube-system
rules:
- apiGroups: ["", "apps"]
resources: ["deployments", "replicasets", "pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: eli-rolebinding
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: User
name: eli
apiGroup: ""
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: eli-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 验证
$ kubectl get deploy,rs,pod --context=eli-context
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/calico-kube-controllers 1/1 1 1 23h
deployment.apps/coredns 2/2 2 2 23h
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/calico-kube-controllers-654b987fd9 1 1 1 23h
replicaset.apps/coredns-59d64cd4d4 2 2 2 23h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/calico-kube-controllers-654b987fd9-86w7m 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/calico-node-5z74f 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/calico-node-bttbd 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/calico-node-gbgrz 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/coredns-59d64cd4d4-47jd5 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/coredns-59d64cd4d4-68zj9 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/etcd-k8s-master 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/kube-apiserver-k8s-master 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/kube-controller-manager-k8s-master 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/kube-proxy-47cwt 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/kube-proxy-6g99p 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/kube-proxy-btjdf 1/1 Running 0 23h
pod/kube-scheduler-k8s-master 1/1 Running 0 23h
3.5.2 ServiceAccount (namespace)
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: eli-sa
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: eli-sa-role
namespace: kube-system
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: eli-sa-rolebinding
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: eli-sa
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: eli-sa-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
验证:
# 获取新建的SA信息
$ kubectl get secret -n kube-system | grep eli-sa
eli-sa-token-rltqf kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 39s
# 获取该SA的JWT,可使用它来作为Dashboard登录凭证
$ kubectl get secret eli-sa-token-rltqf -o jsonpath={.data.token} -n kube-system | base64 -d
注意:该 JWT 只能访问 kube-system 一个命名空间
3.5.3 ServiceAccount (cluster全局)
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: eli-sa
namespace: kube-system
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: eli-sa-clusterrolebinding
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: eli-sa
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin # 集群默认管理角色
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
验证:
# 获取新建的SA信息
$ kubectl get secret -n kube-system | grep eli-sa
eli-sa-token-shhwv kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 35s
# 获取该SA的JWT,可使用它来作为Dashboard登录凭证
$ kubectl get secret eli-sa-token-shhwv -o jsonpath={.data.token} -n kube-system | base64 -d
注意:该 JWT 是全局性的,可访问所有命名空间
4. 准入控制器
准入控制器是一段代码,它会在请求通过认证和授权之后、对象被持久化之前拦截到达 API 服务器的请求。
启用和禁用准入控制器:
kube-apiserver --enable-admission-plugins=NamespaceLifecycle,LimitRanger ...
kube-apiserver --disable-admission-plugins=PodNodeSelector,AlwaysDeny ...
两个特殊的控制器:
- MutatingAdmissionWebhook:执行变更准入控制的 webhook
- ValidatingAdmissionWebhook:执行验证准入控制的 webhook
准入控制过程分为两个阶段,任何一个阶段控制器拒绝请求,则整个请求将立即被拒绝,并向终端返回一个错误:
- 运行变更准入控制器
- 运行验证准入控制器
常见准入控制器:
- AlwaysPullImages:修改 Pod 时,强制重新拉取镜像
- DefaultStorageClass:创建
PersistentVolumeClaim时,不请求任何特定存储类的对象,并自动向其添加默认存储类 - DefaultTolerationSeconds:将Pod的容忍时间
notready:NoExecute和unreachable:NoExecute默认设置为5分钟 - DenyEscalatingExec:拒绝
exec和附加命令到以允许访问宿主机的升级了权限运行的pod - LimitPodHardAntiAffinityTopology:拒绝任何在
requiredDuringSchedulingRequiredDuringExecution的AntiAffinity字段中定义除了kubernetes.io/hostname之外的拓扑关键字的 pod - LimitRanger:确保所有资源请求不会超过 namespace 的
LimitRange。 - MutatingAdmissionWebhook:调用与请求匹配的任何变更 webhook。匹配的 webhook是串行调用的;如果需要,每个人都可以修改对象
- NamespaceAutoProvision:检查命名空间资源上的所有传入请求,并检查引用的命名空间是否存在。如果不存在就创建一个命名空间
- NamespaceExists:此检查除
Namespace其自身之外的命名空间资源上的所有请求。如果请求引用的命名空间不存在,则拒绝该请求 - NamespaceLifecycle:强制执行正在终止的命令空间中不能创建新对象,并确保
Namespace拒绝不存在的请求。它还防止缺失三个系统保留的命名空间default、kube-system、kube-public - NodeRestriction:限制 kubelet 可以修改的
Node和Pod对象 - OwnerReferencesPermissionEnforcement:保护对
metadata.ownerReferences对象的访问,以便只有对该对象具有“删除”权限的用户才能对其进行更改 - PodNodeSelector:通过读取命名空间注释和全局配置来限制可在命名空间内使用的节点选择器
- PodPreset:注入一个pod,其中包含匹配的PodPreset中指定的字段
- PodSecurityPolicy:用于创建和修改pod,并根据请求的安全上下文和可用的Pod安全策略确定是否应该允许它
- PodTolerationRestriction:验证容器的容忍度与其命名空间的容忍度之间是否存在冲突,并在存在冲突时拒绝该容器请求
- Priority:使用
priorityClassName字段并填充优先级的整数值。如果未找到优先级,则拒绝Pod - ResourceQuota:观察传入请求并确保它不违反命名空间的
ResourceQuota对象中列举的任何约束 - SecurityContextDeny:拒绝任何试图设置某些升级的 SecurityContext 字段的pod
- ServiceAccount:实现 ServiceAccounts 的自动化。
- StorageObjectInUseProtection:将
kubernetes.io/pvc-protection或kubernetes.io/pv-protectionfinalizers 添加到新创建的持久化卷声明(PVC) 或持久化卷(PV)中。 如果用户尝试删除 PVC/PV,除非 PVC/PV 的保护控制器移除 finalizers,否则 PVC/PV 不会被删除 - ValidatingAdmissionWebhook:调用与请求匹配的任何验证webhook。匹配的webhooks是并行调用的;如果其中任何一个拒绝请求,则请求失败。
5. Security Context
5.1 概述
kubernetes 提供了三种配置安全上下文级别的方法:
- Container-level Security Context:应用到指定的容器
- Pod-level Security Context:应用到 Pod 内所有容器和 Volume
- Pod Security Policies (PSP):应用到集群内部所有 Pod 以及 Volume
pod.spec.securityContext 字段设置:
| 字段名 | 详细说明 |
|---|---|
| runAsNonRoot | 是否在运行容器前执行检查,以确保容器不以root用户运行(UID为0) |
| runAsUser | 运行容器entrypoint进程的UID,默认为Dockerfile中User指定的用户 |
| runAsGroup | 运行容器entrypoint进程的GID,默认为容器引擎的GID |
| fsGroup | 数据卷GID控制,多个不同的容器操作同一份数据卷时,保存GID统一 |
| supplementalGroups | 运行容器时的GID之外的附加组 |
| seLinuxOptions | 它设定的SELinux上下文将被应用到Pod中的所有容器。如果不指定,容器引擎将随机分配一个 |
| sysctls | 将给定的sysctls应用到Pod容器中 |
| seccompProfile | 限制系统调用 |
pod.spec.containers.securityContext 字段设置:
| 字段名 | 详细说明 |
|---|---|
| runAsNonRoot | 同pod中的设置,同时存在时,以容器为准 |
| runAsUser | 同pod中的设置,同时存在时,以容器为准 |
| runAsGroup | 同pod中的设置,同时存在时,以容器为准 |
| seLinuxOptions | 同pod中的设置,同时存在时,以容器为准 |
| capabilities | 给某个特定的进行超级权限,而不用给root用户所有的 privileged 权限 |
| allowPrivilegeEscalation | 定义了一个进程是否可以比其父进程获得更多的特权 |
| privileged | 以特权模式运行 |
| seccompProfile | 限制系统调用 |
5.2 Linux Capabilities
Linux 将传统上与超级用户 root 关联的特权划分为不同的单元,称为 capabilites。它的每个单元都可以独立启用和禁用。系统在作权限检查时:在执行特权操作时,如果进程的有效身份不是 root,就去检查是否具有该特权操作所对应的 capabilites,并以此决定是否可以进行该特权操作。详细说明:https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/capabilities.7.html
使用 Capabilities:
$ getcap /bin/ping
/bin/ping = cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw+p
$ sudo setcap cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw-p /bin/ping
$ getcap /bin/ping
/bin/ping =
$ ping www.baidu.com
ping: socket: Operation not permitted
可执行文件的属性中有三个集合来保存三类 capabilities:
- Permitted:在进程执行时,Permitted 集合中的 capabilites 自动被加入到进程的 Permitted 集合中。
- Inheritable:Inheritable 集合中的 capabilites 会与进程的 Inheritable 集合执行与操作,以确定进程在执行 execve 函数后哪些 capabilites 被继承。
- Effective:Effective 只是一个 bit。如果设置为开启,那么在执行 execve 函数后,Permitted 集合中新增的 capabilities 会自动出现在进程的 Effective 集合中
5.3 实例
5.3.1 Pod Security Context
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-sec-ctx
spec:
volumes:
- name: sec-ctx-vol
emptyDir: {}
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
runAsGroup: 3000
fsGroup: 2000
containers:
- name: sec-ctx-demo
image: busybox
command: ["sh", "-c", "sleep 3600"]
volumeMounts:
- name: sec-ctx-vol
mountPath: /mnt/data # 该数据卷下创建的文件,其 GID 为2000
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
验证:
$ kubectl exec -it pod-sec-ctx -- top
Mem: 3706896K used, 331828K free, 1804K shrd, 266016K buff, 2729800K cached
CPU: 2.5% usr 2.5% sys 0.0% nic 95.0% idle 0.0% io 0.0% irq 0.0% sirq
Load average: 1.93 0.99 0.40 2/397 13
PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %VSZ CPU %CPU COMMAND
7 0 1000 R 1324 0.0 0 0.0 top
1 0 1000 S 1312 0.0 0 0.0 sleep 3600
$ kubectl exec -it pod-sec-ctx -- id
uid=1000 gid=3000 groups=2000
$ kubectl exec -it pod-sec-ctx -- ls -l /mnt
total 4
drwxrwsrwx 2 root 2000 4096 Feb 27 07:12 data
5.3.2 容器 Security Context
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: container-sec-ctx
spec:
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
containers:
- name: sec-ctx-demo
image: busybox
command: [ "sh", "-c", "sleep 3600" ]
securityContext:
runAsUser: 2000
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
验证:
$ kubectl exec -it container-sec-ctx -- top
Mem: 3268492K used, 770232K free, 1644K shrd, 284924K buff, 2115456K cached
CPU: 0.8% usr 0.6% sys 0.0% nic 98.4% idle 0.0% io 0.0% irq 0.0% sirq
Load average: 0.17 0.16 0.11 2/361 12
PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %VSZ CPU %CPU COMMAND
7 0 2000 R 1324 0.0 2 0.0 top
1 0 2000 S 1312 0.0 2 0.0 sleep 3600
5.3.3 Capabilities
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: container-sec-ctx-cap
spec:
containers:
- name: cpb
image: busybox
args:
- sleep
- "3600"
securityContext:
capabilities:
add:
- NET_ADMIN
drop:
- KILL
6. 普通用户管理集群
6.1 创建用户
# 创建 namespace
kubectl create ns eli
# 创建用户
useradd -s /bin/bash -d /home/eli -m eli
su - eli
$ kubectl get pod
The connection to the server localhost:8080 was refused - did you specify the right host or port?
6.2 创建证书
mkdir -p /root/certs && cd $_
cat > eli-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "eli",
"hosts": [],
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "Nanjing",
"O": "k8s",
"ST": "Jiangsu",
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
EOF
cd /etc/kubernetes/pki
cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -profile=kubernetes /root/certs/eli-csr.json | cfssljson -bare eli
6.3 生成集群配置
cd /root/certs
export KUBE_APISERVER="https://192.168.80.240:6443"
# 创建 kubeconfig
kubectl config set-cluster kubernetes \
--certificate-authority=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.pem \
--embed-certs=true --server=${KUBE_APISERVER} \
--kubeconfig=eli.kubeconfig
# 设置客户端参数,绑定用户到 kubeconfig
kubectl config set-credentials eli \
--client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/pki/eli.pem \
--client-key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/eli-key.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--kubeconfig=eli.kubeconfig
# 设置上下文
kubectl config set-context kubernetes \
--cluster=kubernetes \
--user=eli \
--namespace=eli \
--kubeconfig=eli.kubeconfig
6.4 创建角色并绑定
cat > eli-role.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: admin
namespace: eli
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get","list","create","update","patch","delete","watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin
namespace: eli
subjects:
- kind: User
name: eli
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
EOF
kubectl apply -f eli-role.yml
6.5 验证权限
# 复制配置
mkdir -p /home/eli/.kube
cp eli.kubeconfig /home/eli/.kube/config
chown -R eli:eli /home/eli/.kube
# 切换用户
su - eli
# 切换上下文,使 Kubectl 读取到config 信息
$ kubectl config use-context kubernetes --kubeconfig=.kube/config
# 验证
$ kubectl get pod
No resources found in eli namespace.
$ kubectl get svc
Error from server (Forbidden): services is forbidden: User "eli" cannot list resource "services" in API group "" in the namespace "eli"
# 创建 deployment
$ kubectl create deployment nginx --replicas=10 --image=nginx --port-80
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-7848d4b86f-2j7lt 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-89l2d 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-9tf57 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-bhhz2 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-ft7fv 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-l7vqn 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-qrkvh 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-sjpch 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-wvm4n 1/1 Running 0 86s
nginx-7848d4b86f-xwnsf 1/1 Running 0 86s
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容









所有评论(0)