SpringBoot项目main方法详解
前言SpringBoot项目启动时通过执行main方法启动,main方法主要做了两方面工作:初始化Spring容器启动tomcat运行项目下面我们通过源码来看如何进行的上面两个操作。源码分析我们以debug的方式进行源码的分析。main方法中,我们调用了SpringApplication的run方法启动项目,我们看run方法的源码:public ConfigurableApplicationCon
前言
SpringBoot项目启动时通过执行main方法启动,main方法主要做了两方面工作:
- 初始化Spring容器
- 启动tomcat运行项目
下面我们通过源码来看如何进行的上面两个操作。
源码分析
我们以debug的方式进行源码的分析。main方法中,我们调用了SpringApplication的run方法启动项目,我们看run方法的源码:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
在如下代码中,创建了上下文对象:
context = createApplicationContext();
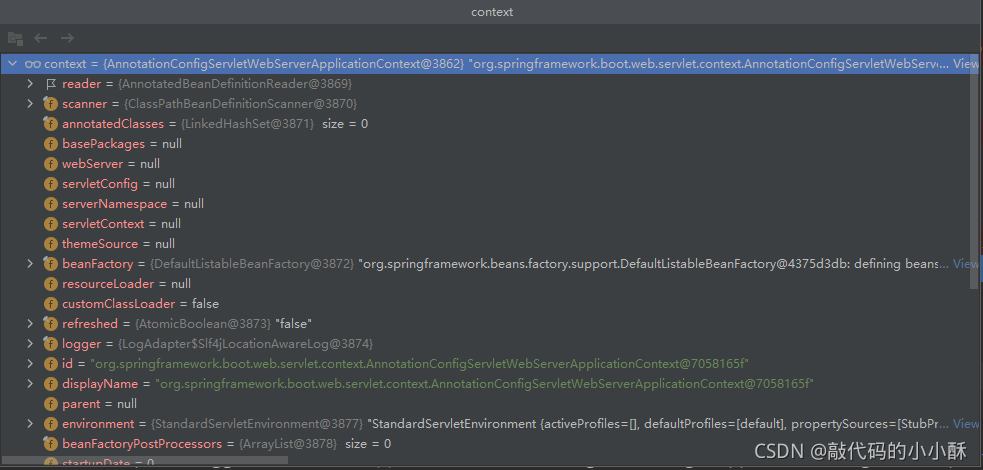
可以看到,在SpringBoot中,使用的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类作为上下文对象,它也是ApplicationContext的一个子类。
所以,当调用如下代码时:
refreshContext(context);
最终,走入了ApplicationContext的refresh方法中,进行了Spring容器的启动。
在Spring的refresh方法中,应用了模板设计模式,其内部的onRefresh方法就是个钩子方法,让子类进行实现。我们上面提到,SpringBoot用了AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext作为上下文对象,所以最终调用的是这个类的onRefresh方法。我们看这个方法源码:
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
在createWebServer方法中往下追代码,最终追到getWebServer方法,看其源码:
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
可以看到,这里采用编程式的tomcat,进行了启动。 我们也可以自己new出一个Tomcat来,进行tomcat的运行。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献17条内容
已为社区贡献17条内容









所有评论(0)