Springboot优雅停机-Springboot的shutdown实现
Springboot优雅停机
以下内容基于springboot 2.6.4,jdk-17.0.2版本
导言:
在很多情况,在应用程序启动后需要关闭的时候,直接对着窗口就是X或者直接KILL -9,这种关闭方式会导致部分正在处理的请求中断,业务停留于不可控业务过程中,可能会引起数据与业务不一致的情况。而正常的做法我们应该使用优雅关机方式,即不再接收新的请求,并将已接受到的请求处理完毕,再关闭程序,释放资源。如Ctrl+C或Kill-2。
Springboot graceful shutdown 应用场景:
在Springboot中,提供了优雅停机方案,内嵌到Springboot中的4个Web服务器(Jetty,Reactor Netty,Tomcat,Undertow)与反应式和基于servlet的web应用程序,在停止SmartLifecycle的早期阶段会逐步停止应用程序上下文。这个过程中,会给应用程序一个宽限期,然后不再处理新的请求处理,并将已接受到的请求在宽限期内结束,而对触发停机后再接收到的请求处理方式取决于不同的web服务器。Jetty,Reactor Netty,Tomcat将会在网络层停止请求接收,而Undertow将会接收请求,但会直接返回服务器不可用的503状态码。
优雅停机需要Tomcat 9.0.33及以上
使用方式:
开启优雅停机,需要配置server.shutdown属性,如:
server:
shutdown: “graceful”还需要配置一个宽限期配置,如:
spring:
lifecycle:
timeout-per-shutdown-phase: “20s”(以上资料来源于:Spring Boot Reference Documentation v2.6.4 # 8.3 Graceful Shutdown)
原理分析:
SpringBoot在运行创建ApplicationContext时,会通过refreshContext 方法将context注册到shutdown钩子上,再通过SpringApplicationShutdownHook的addRuntimeShutdownHookIfNecessary 方法使用Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook 将SpringApplicationShutdownHook注入到Java的Shutdown中的,建立关系。
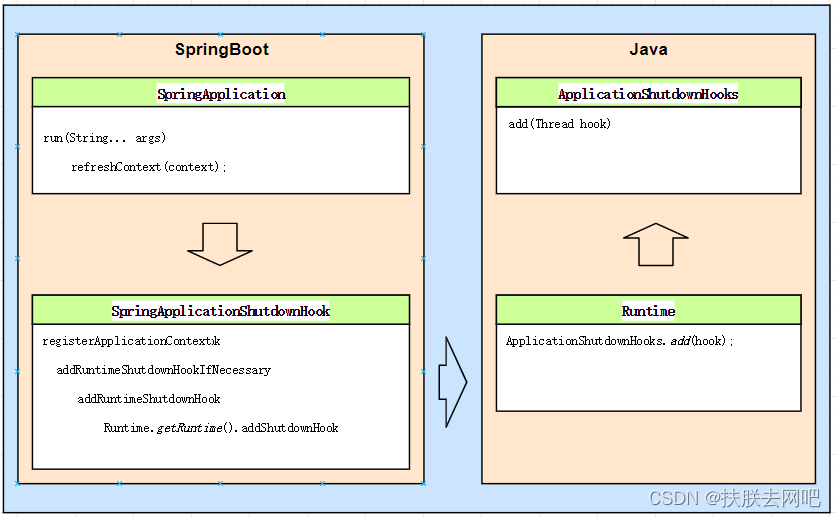
详细:
1. SpringBoot启动,SpringApplication类创建ApplicationContext,调用refreshContext方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//1.调用refreshContext方法
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}2. 在方法中,会先检查是否注册shutdown钩子的开关,若开关打开,则会将context注册到shutdown钩子中,
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
//注册到钩子
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
refresh(context);
}3. 上一步中,SpringApplication调用的是SpringApplicationShutdownHook的registerApplicationContext方法,在这个方法中,会将其加入到运行时Shutdown钩子中,并开启监听,再将上下文关联到当前contexts中(用于关闭)。
void registerApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//通过Runtime调用
addRuntimeShutdownHookIfNecessary();
synchronized (SpringApplicationShutdownHook.class) {
assertNotInProgress();
//加入监听
context.addApplicationListener(this.contextCloseListener);
//保存上下文
this.contexts.add(context);
}
}4. 我们重点看addRuntimeShutdownHookIfNecessary方法,这个方法主要是通过Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook将SpringApplicationShutdownHook加入到java的shutdown钩子中。
private final AtomicBoolean shutdownHookAdded = new AtomicBoolean();
private void addRuntimeShutdownHookIfNecessary() {
if (this.shutdownHookAdded.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
addRuntimeShutdownHook();
}
}
void addRuntimeShutdownHook() {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(this, "SpringApplicationShutdownHook"));
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments
}
}几个重点:
1.这里用的是AtomicBoolean
2.从这步结束,之前都是Spring的Shutdown钩子处理,之后,都是java中Shutdown钩子处理。
5. 调用运行时的addShutdownHook方法后,会通过ApplicationShutdownHooks.add(hook)方法将钩子添加到java应用程序Shutdown钩子集合中。
public void addShutdownHook(Thread hook) {
@SuppressWarnings("removal")
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("shutdownHooks"));
}
ApplicationShutdownHooks.add(hook);
}6. 在将ApplicationShutdownHooks添加到钩子集合中前,会检查钩子的状态,确认状态无误后,再将钩子加入到集合中。加入集合后,流程结束。
static synchronized void add(Thread hook) {
if(hooks == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress");
if (hook.isAlive())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook already running");
if (hooks.containsKey(hook))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook previously registered");
hooks.put(hook, hook);
}7. 在ApplicationShutdownHooks有个静态方法会调用Shutdown初始化钩子集合。
private static IdentityHashMap<Thread, Thread> hooks;
static {
try {
Shutdown.add(1 /* shutdown hook invocation order */,
false /* not registered if shutdown in progress */,
new Runnable() {
public void run() {
runHooks();
}
}
);
hooks = new IdentityHashMap<>();
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
// application shutdown hooks cannot be added if
// shutdown is in progress.
hooks = null;
}
}这里有个地方有点意思:这里的钩子用的是IdentityHashMap存储,意味着能将两个‘相同’的钩子加入到钩子集合中。
这章说了Springboot的Shutdown实现,下一章再将Java的Shutdown详细说说。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)