yolov3训练自己的数据集
yolov3训练自己的数据集
最近在学图像识别,跑了几遍yolov3,在此做一些记录
我的环境如下:
ubuntu: 18.04
GPU: RTX3050ti
cuda: 11.4
cudnn: 8.4.1
opencv: 4.2
python: 3.6.9首先是框架的安装,我选择的是AB大神的darknet框架,下载过程如下:
git clone https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet.git
cd darknet修改一下makefile文件
GPU=1//GPU=1表示启用GPU
CUDNN=1//CUDNN=1表示启用cudnn
CUDNN_HALF=0
OPENCV=1//opencv=1表示启用opencv,如果需要调用摄像头需启用
AVX=0
OPENMP=0
LIBSO=0
ZED_CAMERA=0
ZED_CAMERA_v2_8=0
# set GPU=1 and CUDNN=1 to speedup on GPU
# set CUDNN_HALF=1 to further speedup 3 x times (Mixed-precision on Tensor Cores) GPU: Volta, Xavier, Turing and higher
# set AVX=1 and OPENMP=1 to speedup on CPU (if error occurs then set AVX=0)
# set ZED_CAMERA=1 to enable ZED SDK 3.0 and above
# set ZED_CAMERA_v2_8=1 to enable ZED SDK 2.X
我的建议是一定要用cuda,纯CPU跑的特别慢,可以考虑云GPU
编译:
make下载yolov3预训练模型:(如果下载的很慢的话可以从博主的这篇博客下载)
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights测试一下是否安装好了:
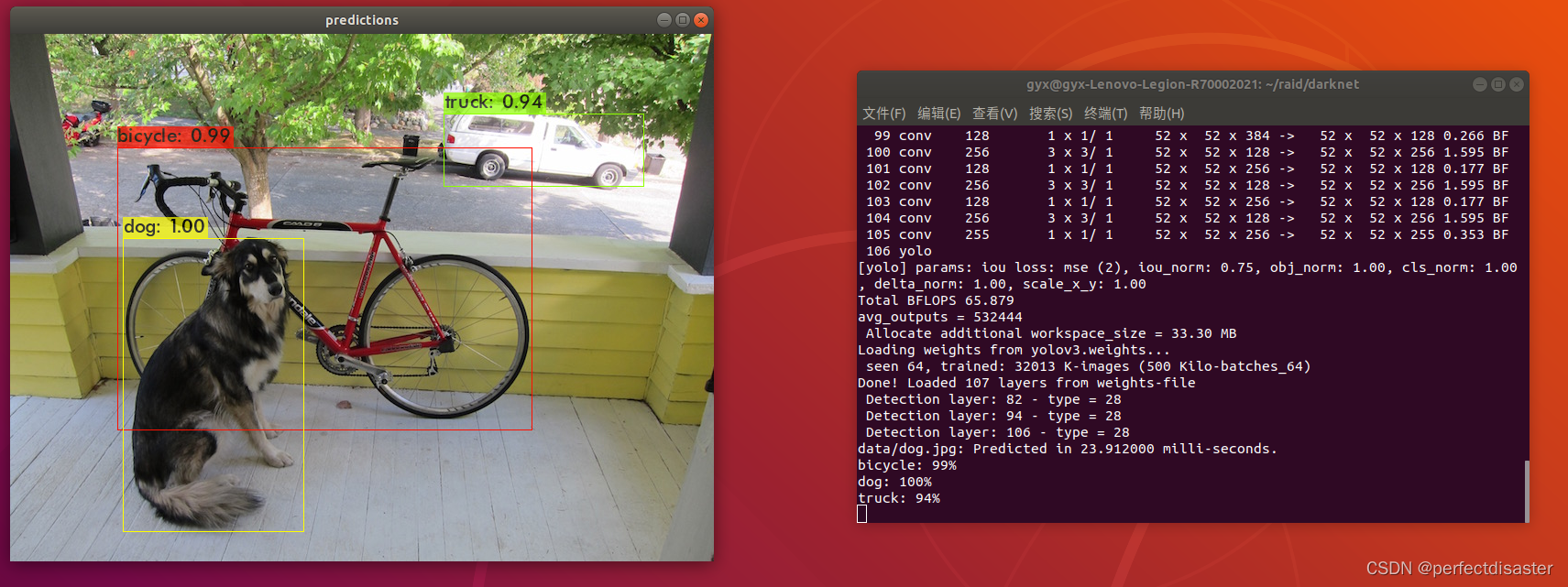
./darknet detect cfg/yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights data/dog.jpg
或者
./darknet detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights data/dog.jpg运行结果如下时,恭喜你安装成功了
接下来就可以着手训练自己的数据集了
一.训练数据集的第一步首先是标注图像,我这里选用的是labelImg,下载地址,安装成功后终端输入:(建议使用conda虚拟环境)
labelImg打开标注界面如下:
yolo使用的文本格式是txt文件,但你也可以标注为xml文件,之后再进行转换即可
二.接下来在darknet目录下创建myData文件夹,目录结构如下,将之前标注好的图片和xml文件放到对应目录下
myData
...JPEGImages#存放图像
...ImageSets/Main #(如果标注的是xml文件的话需创建,txt文件不需要)
...Annotations#存放图像对应的xml文件(如果标注的是xml文件的话)
...labels #存放图像对应的txt文件
...backup #存放训练所得的权重文件三.数据集的配置
1.如果标注的是xml文件,新建my_labels.py文件,复制以下内容:这里参考
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.1
train_percent = 0.9
#xmlfilepath = 'Annotations'
filepath = 'labels'
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets\Main'
#total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
total = os.listdir(filepath)
#num = len(total_xml)
num = len(total)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
#name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
name = total[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()运行:
python my_labels.py会生成labels文件夹,里面放的是对应的txt文件 ;同时在 ImageSets/Main路径下会生成train.txt和test.txt文件
2.如果标注的是txt格式,新建labels.py文件,复制以下内容:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 此代码和myData文件夹同目录
import glob
import os, random, shutil
import sys, getopt
import string
# train, test, rate = getDir(sys.argv[1:])
# if tmp <= 0.0 or tmp >= 1.0:
# rate = 0.1
def moveFile(trainDir, testDir, rate):
rate=float(rate)
pathDir = os.listdir(trainDir) #返回指定的文件夹包含的文件或文件夹的名字的列表
filenumber=len(pathDir)
print("filenumber = ", filenumber)
picknumber=int(filenumber*rate)
print("picknumber = ", picknumber)
sample = random.sample(pathDir, picknumber) #从pathDir中随机选取picknumber个元素
for name in sample:
shutil.move(os.path.join(trainDir,name), os.path.join(testDir,name))
return
train_list = []
test_list = []
train_file = 'train.txt'
test_file = 'test.txt'
rate = 0.80
if __name__ == '__main__':
rate = float(rate)
#pathDir = os.listdir('labels/')
pathDir = os.listdir('/home/your/darknet/myData/JPEGImages/')#改为你自己的路径
filenumber = len(pathDir)
picknumber = int(filenumber * rate)
sample = random.sample(pathDir, picknumber)
for name in sample:
train_list.append(name)
for name in pathDir:
if name not in sample:
test_list.append(name)
cur_dir = os.getcwd() #返回当前进程的工作目录
train_images_dir = os.path.join(cur_dir, 'JPEGImages/')
with open(train_file, 'w') as train_txt:
for name in train_list:
jpg_name = name.strip()
jpg_file = os.path.join(train_images_dir, jpg_name)
train_txt.write(jpg_file + '\n')
train_txt.close()
with open(test_file, 'w') as test_txt:
for name in test_list:
jpg_name = name.strip()
jpg_file = os.path.join(train_images_dir, jpg_name)
test_txt.write(jpg_file + '\n')
test_txt.close()
print(filenumber,picknumber,filenumber-picknumber)运行:
python labels.py
会在myData文件夹下生成test.txt和train.txt文件
3.在myData文件夹下新建myData.names文件,内容如下:
#根据自己的数据集标注的标签,按照序号顺序填写
tissue
roll-of-paper
battled-drinks
chewing-gum
banana四.cfg文件和data文件的修改
在cfg文件夹中创建my_data.data文件,复制以下内容:
classes= 5 ##改为自己的分类个数
##下面都改为自己的路径
train = /home/your/darknet/myData/train.txt #你的train.txt和test.txt在哪里就改成相应路径
valid = /home/your/darknet/myData/test.txt
names = /home/your/darknet/myData/myData.names
backup = /home/your/darknet/myData/backup/复制cfg文件夹中的yolov3.cfg
以下是cfg文件参数详解,参考
我的显卡只能支持batch=64时subdvision=64,如果出现cuda out of memory错误,可以减小batch或增大subdvision ;max_batches根据个人需求修改,如果数据集不大的话可以设置小一些,我的数据集100-500张图片的基本都在1200左右达到不错的效果,1500-1800左右收敛,所以当数据集不大时可以考虑修改为2000,这是我自己的拙见。
[net]
# Testing 测试模式
# batch=1
# subdivisions=1
# Training 训练模式
batch=64 一批训练样本的样本数量,每batch个样本更新一次参数
subdivisions=16 batch/subdivisions作为一次性送入训练器的样本数量,如果内存不够大,将batch分割为subdivisions个子batch
上面这两个参数如果电脑内存小,则把batch改小一点,batch越大,训练效果越好
subdivisions越大,可以减轻显卡压力
width=416 input图像的宽
height=416 input图像的高
channels=3 input图像的通道数
以上三个参数为输入图像的参数信息 width和height影响网络对输入图像的分辨率,
从而影响precision,只可以设置成32的倍数
momentum=0.9 [?]DeepLearning1中最优化方法中的动量参数,这个值影响着梯度下降到最优值得速度https://nanfei.ink/2018/01/23/YOLOv2%E8%B0%83%E5%8F%82%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/#more
decay=0.0005 [?]权重衰减正则项,防止过拟合.每一次学习的过程中,将学习后的参数按照固定比例进行降低,为了防止过拟合,decay参数越大对过拟合的抑制能力越强。
angle=0 通过旋转角度来生成更多训练样本
saturation = 1.5 通过调整饱和度来生成更多训练样本
exposure = 1.5 通过调整曝光量来生成更多训练样本
hue=.1 通过调整色调来生成更多训练样本
learning_rate=0.001 学习率决定着权值更新的速度,设置得太大会使结果超过最优值,太小会使下降速度过慢。
如果仅靠人为干预调整参数,需要不断修改学习率。刚开始训练时可以将学习率设置的高一点,
而一定轮数之后,将其减小
在训练过程中,一般根据训练轮数设置动态变化的学习率。
刚开始训练时:学习率以 0.01 ~ 0.001 为宜。
一定轮数过后:逐渐减缓。
接近训练结束:学习速率的衰减应该在100倍以上。
学习率的调整参考https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33485434/article/details/80452941
burn_in=1000 在迭代次数小于burn_in时,其学习率的更新有一种方式,大于burn_in时,才采用policy的更新方式
max_batches = 20200 训练达到max_batches后停止学习
policy=steps 这个是学习率调整的策略,有policy:constant, steps, exp, poly, step, sig, RANDOM,constant等方式
参考https://nanfei.ink/2018/01/23/YOLOv2%E8%B0%83%E5%8F%82%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/#more
steps=40000,45000 下面这两个参数steps和scale是设置学习率的变化,比如迭代到40000次时,学习率衰减十倍。
scales=.1,.1 45000次迭代时,学习率又会在前一个学习率的基础上衰减十倍
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1 是否做BN
filters=32 输出特征图的数量
size=3 卷积核的尺寸
stride=1 做卷积运算的步长
pad=1 如果pad为0,padding由 padding参数指定;如果pad为1,padding大小为size/2,padding应该是对输入图像左边缘拓展的像素数量
activation=leaky 激活函数的类型
# Downsample
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=64
size=3
stride=2
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=32
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=64
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[shortcut]
from=-3
activation=linear
# Downsample
......
# Downsample
######################
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
filters=45 每一个[region/yolo]层前的最后一个卷积层中的 filters=(classes+1+coords)*anchors_num,
其中anchors_num 是该层mask的一个值.如果没有mask则 anchors_num=num是这层的ancho
5的意义是5个坐标,论文中的tx,ty,tw,th,to
activation=linear
[yolo] 在yoloV2中yolo层叫region层
mask = 6,7,8 这一层预测第6、7、8个 anchor boxes ,每个yolo层实际上只预测3个由mask定义的anchors
anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326
[?]anchors是可以事先通过cmd指令计算出来的,是和图片数量,width,height以及cluster(应该就是下面的num的值,
即想要使用的anchors的数量)相关的预选框,可以手工挑选,也可以通过kmeans 从训练样本中学出
classes=10 网络需要识别的物体种类数
num=9 每个grid cell预测几个box,和anchors的数量一致。当想要使用更多anchors时需要调大num,且如果调大num后训练时Obj趋近0的话可以尝试调大object_scale
jitter=.3 [?]利用数据抖动产生更多数据,YOLOv2中使用的是crop,filp,以及net层的angle,flip是随机的,
jitter就是crop的参数,tiny-yolo-voc.cfg中jitter=.3,就是在0~0.3中进行crop
ignore_thresh = .5 决定是否需要计算IOU误差的参数,大于thresh,IOU误差不会夹在cost function中
truth_thresh = 1
random=0 如果为1,每次迭代图片大小随机从320到608,步长为32,如果为0,每次训练大小与输入大小一致
[route]
layers = -4
......
#可以添加没有标注框的图片和其空的txt文件,作为negative数据
#可以在第一个[yolo]层之前的倒数第二个[convolutional]层末尾添加 stopbackward=1,以此提升训练速度
#即使在用416*416训练完之后,也可以在cfg文件中设置较大的width和height,增加网络对图像的分辨率,从而更可能检测出图像中的小目标,而不需要重新训练
#Out of memory的错误需要通过增大subdivisions来解决修改yolo层和yolo层上的convolutional层的参数,具体为:
convolutional层中:
filters=(classes+1+coords)*anchors_num 一般为filters=(classes+5)*3
yolo层中
classes=数据集中的物体个数
#一共要改3处可以改变yolo层中的anchor的值使结果精度更高,但改不改好像没什么区别,如果要修改的话,在myData文件夹下新建anchors.py文件,复制以下内容:参考
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import random
import argparse
import os
#参数名称
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='使用该脚本生成YOLO-V3的anchor boxes\n')
parser.add_argument('--input_annotation_txt_dir',required=True,type=str,help='输入存储图片的标注txt文件(注意不要有中文)')
parser.add_argument('--output_anchors_txt',required=True,type=str,help='输出的存储Anchor boxes的文本文件')
parser.add_argument('--input_num_anchors',required=True,default=6,type=int,help='输入要计算的聚类(Anchor boxes的个数)')
parser.add_argument('--input_cfg_width',required=True,type=int,help="配置文件中width")
parser.add_argument('--input_cfg_height',required=True,type=int,help="配置文件中height")
args = parser.parse_args()
'''
centroids 聚类点 尺寸是 numx2,类型是ndarray
annotation_array 其中之一的标注框
'''
def IOU(annotation_array,centroids):
#
similarities = []
#其中一个标注框
w,h = annotation_array
for centroid in centroids:
c_w,c_h = centroid
if c_w >=w and c_h >= h:#第1中情况
similarity = w*h/(c_w*c_h)
elif c_w >= w and c_h <= h:#第2中情况
similarity = w*c_h/(w*h + (c_w - w)*c_h)
elif c_w <= w and c_h >= h:#第3种情况
similarity = c_w*h/(w*h +(c_h - h)*c_w)
else:#第3种情况
similarity = (c_w*c_h)/(w*h)
similarities.append(similarity)
#将列表转换为ndarray
return np.array(similarities,np.float32) #返回的是一维数组,尺寸为(num,)
'''
k_means:k均值聚类
annotations_array 所有的标注框的宽高,N个标注框,尺寸是Nx2,类型是ndarray
centroids 聚类点 尺寸是 numx2,类型是ndarray
'''
def k_means(annotations_array,centroids,eps=0.00005,iterations=200000):
#
N = annotations_array.shape[0]#C=2
num = centroids.shape[0]
#损失函数
distance_sum_pre = -1
assignments_pre = -1*np.ones(N,dtype=np.int64)
#
iteration = 0
#循环处理
while(True):
#
iteration += 1
#
distances = []
#循环计算每一个标注框与所有的聚类点的距离(IOU)
for i in range(N):
distance = 1 - IOU(annotations_array[i],centroids)
distances.append(distance)
#列表转换成ndarray
distances_array = np.array(distances,np.float32)#该ndarray的尺寸为 Nxnum
#找出每一个标注框到当前聚类点最近的点
assignments = np.argmin(distances_array,axis=1)#计算每一行的最小值的位置索引
#计算距离的总和,相当于k均值聚类的损失函数
distances_sum = np.sum(distances_array)
#计算新的聚类点
centroid_sums = np.zeros(centroids.shape,np.float32)
for i in range(N):
centroid_sums[assignments[i]] += annotations_array[i]#计算属于每一聚类类别的和
for j in range(num):
centroids[j] = centroid_sums[j]/(np.sum(assignments==j))
#前后两次的距离变化
diff = abs(distances_sum-distance_sum_pre)
#打印结果
print("iteration: {},distance: {}, diff: {}, avg_IOU: {}\n".format(iteration,distances_sum,diff,np.sum(1-distances_array)/(N*num)))
#三种情况跳出while循环:1:循环20000次,2:eps计算平均的距离很小 3:以上的情况
if (assignments==assignments_pre).all():
print("按照前后两次的得到的聚类结果是否相同结束循环\n")
break
if diff < eps:
print("按照eps结束循环\n")
break
if iteration > iterations:
print("按照迭代次数结束循环\n")
break
#记录上一次迭代
distance_sum_pre = distances_sum
assignments_pre = assignments.copy()
if __name__=='__main__':
#聚类点的个数,anchor boxes的个数
num_clusters = args.input_num_anchors
#索引出文件夹中的每一个标注文件的名字(.txt)
names = os.listdir(args.input_annotation_txt_dir)
#标注的框的宽和高
annotations_w_h = []
for name in names:
txt_path = os.path.join(args.input_annotation_txt_dir,name)
#读取txt文件中的每一行
f = open(txt_path,'r')
for line in f.readlines():
line = line.rstrip('\n')
w,h = line.split(' ')[3:]#这时读到的w,h是字符串类型
#eval()函数用来将字符串转换为数值型
annotations_w_h.append((eval(w),eval(h)))
f.close()
#将列表annotations_w_h转换为numpy中的array,尺寸是(N,2),N代表多少框
annotations_array = np.array(annotations_w_h,dtype=np.float32)
N = annotations_array.shape[0]
#对于k-means聚类,随机初始化聚类点
random_indices = [random.randrange(N) for i in range(num_clusters)]#产生随机数
centroids = annotations_array[random_indices]
#k-means聚类
k_means(annotations_array,centroids,0.00005,200000)
#对centroids按照宽排序,并写入文件
widths = centroids[:,0]
sorted_indices = np.argsort(widths)
anchors = centroids[sorted_indices]
#将anchor写入文件并保存
f_anchors = open(args.output_anchors_txt,'w')
#
for anchor in anchors:
f_anchors.write('%d,%d'%(int(anchor[0]*args.input_cfg_width),int(anchor[1]*args.input_cfg_height)))
f_anchors.write('\n')五.开始训练
1.下载预训练文件(有的话更好,没有也能跑)终端输入: (如果下载的很慢的话可以从博主的这篇博客下载)
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/darknet53.conv.742.开始训练,终端输入:
./darknet detector train cfg/my_data.data cfg/my_yolov3.cfg darknet53.conv.74
或者指定gpu训练,默认使用gpu0
./darknet detector train cfg/my_data.data cfg/my_yolov3.cfg darknet53.conv.74 -gups 0,1,2,33.等待训练完成,在myData文件夹下的backup文件夹(需要自己创建)中寻找这一炉仙丹吧
4.如果中途因为out of memory中断进程,修改batches和subdvision 重新训练,从中断处开始训练:
./darknet detector train cfg/my_data.data cfg/my_yolov3.cfg myData/backup/my_yolov3.backup -gpus 0,1,2,3我的效果图(1200的时候有点事退出去了,最后效果还可以,但avg loss达到0.06左右效果更好:
六.测试
终端输入:
#图片测试,视频检测同理
./darknet detector test cfg/my_data.data cfg/my_yolov3.cfg myData/backup/my_yolov3_last.weights 1.jpg
#1.jpg改为图片路径+图片名,我直接在darknet文件夹下检测的,所以没有加路径
#或者运行darknet文件夹下的darknet_images.py文件,记得修改路径
python3 darknet_images.py
#摄像头测试
./darknet detector demo cfg/my_data.data cfg/my_yolov3.cfg myData/backup/my_yolov3_last.weights 我的最终效果:
七.批量测试
在darknet文件夹下创建detect.py,复制以下内容(注意修改为自己的路径):
import argparse
import os
import glob
import random
import darknet
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import darknet
def parser():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="YOLO Object Detection")
parser.add_argument("--input", type=str, default="",
help="image source. It can be a single image, a"
"txt with paths to them, or a folder. Image valid"
" formats are jpg, jpeg or png."
"If no input is given, ")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", default=1, type=int,
help="number of images to be processed at the same time")
parser.add_argument("--weights", default="myData/backup/my_yolov3_last.weights",#修改为自己的路径
help="yolo weights path")
parser.add_argument("--dont_show", action='store_true',
help="windown inference display. For headless systems")
parser.add_argument("--ext_output", action='store_true',
help="display bbox coordinates of detected objects")
parser.add_argument("--save_labels", action='store_true',
help="save detections bbox for each image in yolo format")
parser.add_argument("--config_file", default="./cfg/my_yolov3.cfg",
help="path to config file")
parser.add_argument("--data_file", default="./cfg/my_data.data",
help="path to data file")
parser.add_argument("--thresh", type=float, default=.25,
help="remove detections with lower confidence")
return parser.parse_args()
def check_arguments_errors(args):
assert 0 < args.thresh < 1, "Threshold should be a float between zero and one (non-inclusive)"
if not os.path.exists(args.config_file):
raise(ValueError("Invalid config path {}".format(os.path.abspath(args.config_file))))
if not os.path.exists(args.weights):
raise(ValueError("Invalid weight path {}".format(os.path.abspath(args.weights))))
if not os.path.exists(args.data_file):
raise(ValueError("Invalid data file path {}".format(os.path.abspath(args.data_file))))
if args.input and not os.path.exists(args.input):
raise(ValueError("Invalid image path {}".format(os.path.abspath(args.input))))
def check_batch_shape(images, batch_size):
"""
Image sizes should be the same width and height
"""
shapes = [image.shape for image in images]
if len(set(shapes)) > 1:
raise ValueError("Images don't have same shape")
if len(shapes) > batch_size:
raise ValueError("Batch size higher than number of images")
return shapes[0]
def load_images(images_path):
"""
If image path is given, return it directly
For txt file, read it and return each line as image path
In other case, it's a folder, return a list with names of each
jpg, jpeg and png file
"""
input_path_extension = images_path.split('.')[-1]
if input_path_extension in ['jpg', 'jpeg', 'png']:
return [images_path]
elif input_path_extension == "txt":
with open(images_path, "r") as f:
return f.read().splitlines()
else:
return glob.glob(
os.path.join(images_path, "*.jpg")) + \
glob.glob(os.path.join(images_path, "*.png")) + \
glob.glob(os.path.join(images_path, "*.jpeg"))
def prepare_batch(images, network, channels=3):
width = darknet.network_width(network)
height = darknet.network_height(network)
darknet_images = []
for image in images:
image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image_resized = cv2.resize(image_rgb, (width, height),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
custom_image = image_resized.transpose(2, 0, 1)
darknet_images.append(custom_image)
batch_array = np.concatenate(darknet_images, axis=0)
batch_array = np.ascontiguousarray(batch_array.flat, dtype=np.float32)/255.0
darknet_images = batch_array.ctypes.data_as(darknet.POINTER(darknet.c_float))
return darknet.IMAGE(width, height, channels, darknet_images)
def image_detection(image_path,network, class_names, class_colors, thresh):
# Darknet doesn't accept numpy images.
# Create one with image we reuse for each detect
width = darknet.network_width(network)
height = darknet.network_height(network)
darknet_image = darknet.make_image(width, height, 3)
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image_resized = cv2.resize(image_rgb, (width, height),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
darknet.copy_image_from_bytes(darknet_image, image_resized.tobytes())
detections = darknet.detect_image(network, class_names, darknet_image, thresh=thresh)
darknet.free_image(darknet_image)
image = darknet.draw_boxes(detections, image_resized, class_colors)
return cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB), detections
def batch_detection(network, images, class_names, class_colors,
thresh=0.25, hier_thresh=.5, nms=.45, batch_size=4):
image_height, image_width, _ = check_batch_shape(images, batch_size)
darknet_images = prepare_batch(images, network)
batch_detections = darknet.network_predict_batch(network, darknet_images, batch_size, image_width,
image_height, thresh, hier_thresh, None, 0, 0)
batch_predictions = []
for idx in range(batch_size):
num = batch_detections[idx].num
detections = batch_detections[idx].dets
if nms:
darknet.do_nms_obj(detections, num, len(class_names), nms)
predictions = darknet.remove_negatives(detections, class_names, num)
images[idx] = darknet.draw_boxes(predictions, images[idx], class_colors)
batch_predictions.append(predictions)
darknet.free_batch_detections(batch_detections, batch_size)
return images, batch_predictions
def image_classification(image, network, class_names):
width = darknet.network_width(network)
height = darknet.network_height(network)
image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image_resized = cv2.resize(image_rgb, (width, height),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
darknet_image = darknet.make_image(width, height, 3)
darknet.copy_image_from_bytes(darknet_image, image_resized.tobytes())
detections = darknet.predict_image(network, darknet_image)
predictions = [(name, detections[idx]) for idx, name in enumerate(class_names)]
darknet.free_image(darknet_image)
return sorted(predictions, key=lambda x: -x[1])
def convert2relative(image, bbox):
"""
YOLO format use relative coordinates for annotation
"""
x, y, w, h = bbox
height, width, _ = image.shape
return x/width, y/height, w/width, h/height
def save_annotations(name, image, detections, class_names):
"""
Files saved with image_name.txt and relative coordinates
"""
file_name = name.split(".")[:-1][0] + ".txt"
with open(file_name, "w") as f:
for label, confidence, bbox in detections:
x, y, w, h = convert2relative(image, bbox)
label = class_names.index(label)
f.write("{} {:.4f} {:.4f} {:.4f} {:.4f}\n".format(label, x, y, w, h))
def batch_detection_example():
args = parser()
check_arguments_errors(args)
batch_size = 3
random.seed(3) # deterministic bbox colors
network, class_names, class_colors = darknet.load_network(
args.config_file,
args.data_file,
args.weights,
batch_size=batch_size
)
image_names = ['data/horses.jpg', 'data/horses.jpg', 'data/eagle.jpg']
images = [cv2.imread(image) for image in image_names]
images, detections, = batch_detection(network, images, class_names,
class_colors, batch_size=batch_size)
for name, image in zip(image_names, images):
cv2.imwrite(name.replace("data/", ""), image)
print(detections)
def get_files(dir, suffix):
res = []
for root, directory, files in os.walk(dir):
for filename in files:
name, suf = os.path.splitext(filename)
if suf == suffix:
#res.append(filename)
res.append(os.path.join(root, filename))
return res
def bbox2points_zs(bbox):
"""
From bounding box yolo format
to corner points cv2 rectangle
"""
x, y, w, h = bbox
xmin = int(round(x - (w / 2)))
xmax = int(round(x + (w / 2)))
ymin = int(round(y - (h / 2)))
ymax = int(round(y + (h / 2)))
return xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
def main():
args = parser()
check_arguments_errors(args)
input_dir = '/home/your/raid/darknet'
config_file = '/home/your/raid/darknet/cfg/my_yolov3.cfg'
data_file = '/home/your/darknet/cfg/my_data.data'
weights = '/home/your/darknet/myData/backup/my_yolov3_last.weights'#修改为自己的路径
random.seed(3) # deterministic bbox colors
network, class_names, class_colors = darknet.load_network(
config_file,
data_file,
weights,
batch_size=args.batch_size
)
src_width = darknet.network_width(network)
src_height = darknet.network_height(network)
#生成保存图片路径文件夹
save_dir = os.path.join(input_dir, 'object_result')
# 去除首位空格
save_dir=save_dir.strip()
# 去除尾部 \ 符号
save_dir=save_dir.rstrip("\\")
# 判断路径是否存在 # 存在 True # 不存在 False
isExists=os.path.exists(save_dir)
# 判断结果
if not isExists:
# 如果不存在则创建目录 # 创建目录操作函数
os.makedirs(save_dir)
print(save_dir+' 创建成功')
else:
# 如果目录存在 则不创建,并提示目录已存在
print(save_dir + ' 目录已存在')
image_list = get_files(input_dir, '.jpg')
total_len = len(image_list)
index = 0
#while True:
for i in range(0, total_len):
image_name = image_list[i]
src_image = cv2.imread(image_name)
cv2.imshow('src_image', src_image)
cv2.waitKey(1)
prev_time = time.time()
image, detections = image_detection(
image_name, network, class_names, class_colors, args.thresh)
#'''
file_name, type_name = os.path.splitext(image_name)
#print(file_name)
#print(file_name.split(r'/'))
print(''.join(file_name.split(r'/')[-1]) + 'bbbbbbbbb')
cut_image_name_list = file_name.split(r'/')[-1:] #cut_image_name_list is list
save_dir_image = os.path.join(save_dir ,cut_image_name_list[0])
if not os.path.exists(save_dir_image):
os.makedirs(save_dir_image)
cut_image_name = ''.join(cut_image_name_list) #list to str
object_count = 0
for label, confidence, bbox in detections:
cut_image_name_temp = cut_image_name + "_{}.jpg".format(object_count)
object_count += 1
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = bbox2points_zs(bbox)
print("aaaaaaaaa x,{} y,{} w,{} h{}".format(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax))
xmin_coordinary = (int)(xmin * src_image.shape[1] / src_width-0.5)
ymin_coordinary = (int)(ymin * src_image.shape[0] / src_height-0.5)
xmax_coordinary = (int)(xmax * src_image.shape[1] / src_width+0.5)
ymax_coordinary = (int)(ymax * src_image.shape[0] / src_height+0.5)
if xmin_coordinary>src_image.shape[1]:
xmin_coordinary = src_image.shape[1]
if ymin_coordinary>src_image.shape[0]:
ymin_coordinary = src_image.shape[0]
if xmax_coordinary>src_image.shape[1]:
xmax_coordinary = src_image.shape[1]
if ymax_coordinary>src_image.shape[0]:
ymax_coordinary = src_image.shape[0]
if xmin_coordinary < 0:
xmin_coordinary = 0
if ymin_coordinary < 0:
ymin_coordinary = 0
if xmax_coordinary < 0:
xmax_coordinary = 0
if ymax_coordinary < 0:
ymax_coordinary = 0
print("qqqqqqqq x,{} y,{} w,{} h{}".format(xmin_coordinary, ymin_coordinary, xmax_coordinary, ymax_coordinary))
out_iou_img = np.full((ymax_coordinary - ymin_coordinary, xmax_coordinary - xmin_coordinary, src_image.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8)
out_iou_img[:,:] = src_image[ymin_coordinary:ymax_coordinary,xmin_coordinary:xmax_coordinary]
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(save_dir_image,cut_image_name_temp),out_iou_img)
#'''
#if args.save_labels:
#if True:
#save_annotations(image_name, image, detections, class_names)
darknet.print_detections(detections, args.ext_output)
fps = int(1/(time.time() - prev_time))
print("FPS: {}".format(fps))
if not args.dont_show:
#cv2.imshow('Inference', image)
cv2.waitKey(1)
#if cv2.waitKey() & 0xFF == ord('q'):
#break
index += 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
# unconmment next line for an example of batch processing
# batch_detection_example()
main()
运行:
python3 detect.py
总结:以上就是我在这段时间的学习心得,主要目的是加深理解,也希望能帮到大家,如果有什么错误,也欢迎各位批评指正,共同进步!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容










所有评论(0)