Python获取网卡信息(名称、MAC、IP、网关等)
“人生苦短,我用Python”。Python的高效有一部分是跟它丰富的模块分不开的。Python有很多第三方模块可以帮助我们完成一些事情,减少开发时间。Python pypi库中一个模块名字叫“netifaces”,使用C语言写的一个第三方模块。可以:1.获取本机的所有网关2.获取本机所有的接口Interface(网卡NIC)3.获取本机指定接口的详细信息,包括IP地址、子网掩码、广播地址、MAC
“人生苦短,我用Python”。Python的高效有一部分是跟它丰富的模块分不开的。Python有很多第三方模块可以帮助我们完成一些事情,减少开发时间。
Python pypi库中一个模块名字叫“netifaces”,使用C语言写的一个第三方模块。可以:
1.获取本机的所有网关
2.获取本机所有的接口Interface(网卡NIC)
3.获取本机指定接口的详细信息,包括IP地址、子网掩码、广播地址、MAC地址等
不过遗憾的是这个模块的功能太有限以及会带出一些令人困惑的信息,例如Windows系统上的子网掩码可能不正确等。
PS:要想获取公网地址,可以使用很多种API,例如:
# Use 3rd party web-sites to get your IP # Please note that I do not recommend following curl/wget method due to security reasons. You have been warned:curl ifconfig.me
curl icanhazip.com
curl ipecho.net/plain
curl ifconfig.co
curl http://ip.chinaz.com/getip.aspx
运行截图如下:
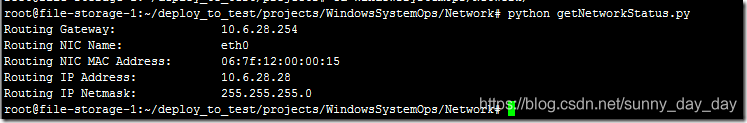
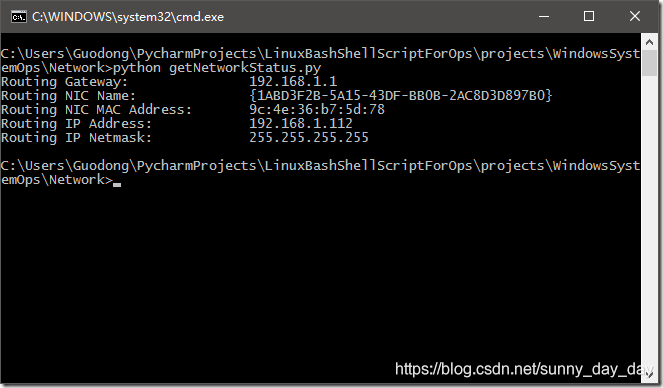
代码请移步到GitHub: https://github.com/DingGuodong/LinuxBashShellScriptForOps/blob/master/projects/WindowsSystemOps/Network/getNetworkStatus.py
代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
# encoding: utf-8
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-
"""
Created by PyCharm.
File: LinuxBashShellScriptForOps:getNetworkStatus.py
User: Guodong
Create Date: 2016/11/2
Create Time: 16:20
show Windows or Linux network Nic status, such as MAC address, Gateway, IP address, etc
# python getNetworkStatus.py
Routing Gateway: 10.6.28.254
Routing NIC Name: eth0
Routing NIC MAC Address: 06:7f:12:00:00:15
Routing IP Address: 10.6.28.28
Routing IP Netmask: 255.255.255.0
"""
import os
import sys
try:
import netifaces
except ImportError:
try:
command_to_execute = "pip install netifaces || easy_install netifaces"
os.system(command_to_execute)
except OSError:
print "Can NOT install netifaces, Aborted!"
sys.exit(1)
import netifaces
routingGateway = netifaces.gateways()['default'][netifaces.AF_INET][0]
routingNicName = netifaces.gateways()['default'][netifaces.AF_INET][1]
for interface in netifaces.interfaces():
if interface == routingNicName:
# print netifaces.ifaddresses(interface)
routingNicMacAddr = netifaces.ifaddresses(interface)[netifaces.AF_LINK][0]['addr']
try:
routingIPAddr = netifaces.ifaddresses(interface)[netifaces.AF_INET][0]['addr']
# TODO(Guodong Ding) Note: On Windows, netmask maybe give a wrong result in 'netifaces' module.
routingIPNetmask = netifaces.ifaddresses(interface)[netifaces.AF_INET][0]['netmask']
except KeyError:
pass
display_format = '%-30s %-20s'
print display_format % ("Routing Gateway:", routingGateway)
print display_format % ("Routing NIC Name:", routingNicName)
print display_format % ("Routing NIC MAC Address:", routingNicMacAddr)
print display_format % ("Routing IP Address:", routingIPAddr)
print display_format % ("Routing IP Netmask:", routingIPNetmask)
最后:不要重复制造轮子。重复制造轮子对自己而言,虽然制造的过程是学习巩固的过程,但重复制造轮子对别人没有好处,人生苦短,别重复制造轮子,除非你制造的足够好。
tag:python获取MAC地址,python获取网关地址,python获取IP地址
–end–
.
.
.
.
.
其他项
.
.
.
获取ip还有种写法:
import socket
import fcntl
import struct
def get_ip_address(ifname):
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
print socket.inet_ntoa(fcntl.ioctl(s.fileno(), 0x8915, struct.pack('256s', ifname[:15]))[20:24])
get_ip_address('lo')
get_ip_address('eth0')
运行结果:
127.0.0.1
10.6.28.2
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import os, time, re, sensors
last_worktime=0
last_idletime=0
sensors.init()
def get_mem_usage_percent():
try:
f = open('/proc/meminfo', 'r')
for line in f:
if line.startswith('MemTotal:'):
mem_total = int(line.split()[1])
elif line.startswith('MemFree:'):
mem_free = int(line.split()[1])
elif line.startswith('Buffers:'):
mem_buffer = int(line.split()[1])
elif line.startswith('Cached:'):
mem_cache = int(line.split()[1])
elif line.startswith('SwapTotal:'):
vmem_total = int(line.split()[1])
elif line.startswith('SwapFree:'):
vmem_free = int(line.split()[1])
else:
continue
f.close()
except:
return None
physical_percent = usage_percent(mem_total - (mem_free + mem_buffer + mem_cache), mem_total)
virtual_percent = 0
if vmem_total > 0:
virtual_percent = usage_percent((vmem_total - vmem_free), vmem_total)
return physical_percent, virtual_percent
def usage_percent(use, total):
try:
ret = (float(use) / total) * 100
except ZeroDivisionError:
raise Exception("ERROR - zero division error")
return ret
def disk_use():
statvfs = os.statvfs('/')
total_disk_space = statvfs.f_frsize * statvfs.f_blocks
free_disk_space = statvfs.f_frsize * statvfs.f_bfree
disk_usage = (total_disk_space - free_disk_space) * 100.0 / total_disk_space
# disk_tip = "硬盘空间使用率:"+str(disk_usage)+"%"
# print(disk_tip)
return disk_usage
def mem_use():
mem_usage = get_mem_usage_percent()
mem_usage = mem_usage[0]
# mem_tip = "物理内存使用率:"+str(mem_usage)+"%"
# print(mem_tip)
return mem_usage
def cpu_use():
global last_worktime, last_idletime
f=open("/proc/stat","r")
line=""
while not "cpu " in line: line=f.readline()
f.close()
spl=line.split(" ")
worktime=int(spl[2])+int(spl[3])+int(spl[4])
idletime=int(spl[5])
dworktime=(worktime-last_worktime)
didletime=(idletime-last_idletime)
rate=float(dworktime)/(didletime+dworktime)
cpu_t = rate*100
last_worktime=worktime
last_idletime=idletime
if(last_worktime==0): return 0
# cpu_tip = "CPU使用率:"+str(cpu_t)+"%"
# print(cpu_tip)
return cpu_t
def cpu_temperature():
for chip in sensors.ChipIterator("coretemp-*"):
i = 0
sum = 0
for feature in sensors.FeatureIterator(chip):
sfi = sensors.SubFeatureIterator(chip, feature)
vals = [sensors.get_value(chip, sf.number) for sf in sfi]
sum = sum + vals[0]
i = i + 1
# cpu_tmp = "CPU温度:"+sum/i+"℃"
# print(cpu_tmp)
return sum/i
disk = disk_use()
print(disk)
print(type(disk))
mem = mem_use()
print(mem)
print(type(mem))
cpua = cpu_use()
print(cpua)
print(type(cpua))
cpub = cpu_temperature()
print(cpub)
print(type(cpub))
sensors.cleanup()
注意:CPU使用率、内存使用率、硬盘使用率都还好说,但是CPU温度就比较麻烦一些了,得使用sensors来整,lm_sensors的软件可以帮助我们来监控主板、CPU的工作电压、风扇转速、温度等数据。这些数据我们通常在主板的BIOS也可以看到。当我们可以在机器运行的时候通过lm_sensors随时来监测着CPU的温度变化,可以预防呵保护因为CPU过热而会烧掉。如果你没有这个模块,使用apt-get install lm-sensors命令来安装即可(我这里使用的是Debian8.6 64位)。
还得和上面的同一目录下再来这么一个文件(https://github.com/paroj/sensors.py/blob/master/sensors.py)
运行代码:
python hui.py
32.1816127961
<type 'float'>
37.7943290638
<type 'float'>
0.251490181586
<type 'float'>
100.0
<type 'float'>
http://www.rojtberg.net/836/introducing-sensors-py/
https://github.com/paroj/sensors.py/blob/master/sensors.py
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献15条内容
已为社区贡献15条内容








所有评论(0)