图神经网络(一)—GraphSAGE-pytorch版本代码详解
GraphSAGE代码详解-pytorch版本1. GraphSAGE导入2. 代码解析2.1 加载数据2.2 Unsupervised Loss2.3 Models2.4 评估与模型使用2.5 Main参考资料1. GraphSAGE导入论文标题:Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs作者:William L. Hamilton, Re
GraphSAGE代码详解-pytorch版本
写在前面…
在研究生的工作中使用到了图神经网络,所以平时会看一些与图神经网络相关的论文和代码。写这个系列的目的是为了帮助自己再理一遍算法的基本思想和流程,如果同时也能对其他人提供帮助是极好的~博主也是在学习过程中,有些地方有误还请大家批评指正!
- github: https://github.com/OuYangg/GNNs
1. GraphSAGE基本介绍
-
论文标题:Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs
-
作者:William L. Hamilton, Rex Ying and Jure Leskovec
在GraphSAGE之前提出的图神经网络方法,如GCN,都属于transductive模型,此类模型在当网络的结构稍微出现一点改变,就需要重新训练,无法满足实时快速产生网络节点嵌入的需求。为了解决这一问题,Jure大佬等人提出了一个infuctive模型,那就是GraphSAGE。GraphSAGE的目标是训练多个aggregator以聚合目标节点不同阶的邻居节点信息,从而可以快速生成未知节点的低维向量表示。
-
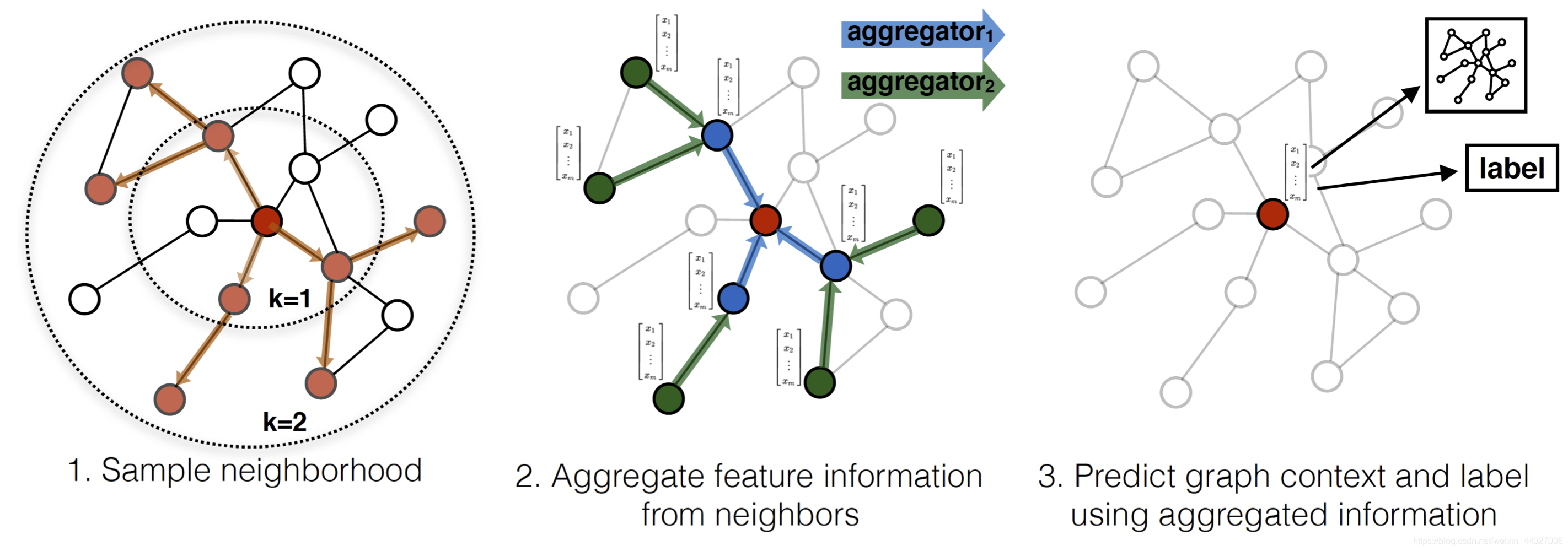
GraphSAGE的基本流程见下图:

1)首先通过随机游走获得固定大小的邻域网络 2)然后通过aggregator把有限阶邻居节点的特征聚合给目标节点,伪代码如下

由上面的伪代码可见,GraphSAGE的输入为:目标网络 G G G、节点的特征向量 x v x_v xv、权重矩阵 W k W^k Wk、非线性激活函数 σ \sigma σ、aggregator函数以及邻居函数 N N N. 1)首先 h 0 h_0 h0为节点的特征向量,循环 K K K步 2)遍历每个节点,对于每个节点首先聚合邻居节点 k − 1 k-1 k−1时刻的特征,然后将聚合的结果与当前节点 k − 1 k-1 k−1时刻的特征进行concat并经过一个激活函数 3)当循环完K步之后进行一个令 h k h_k hk除以 ∣ ∣ h k ∣ ∣ 2 ||h_k||_2 ∣∣hk∣∣2得到节点的低维表示。 -
Aggregators: 从上面的流程图和伪代码可见,GraphSAGE需要用到aggregators,那这个aggregator是什么呢?起到什么作用呢?其实aggregator的作用就是将目标节点的邻居信息进行一个聚合,作者在文中给出了3种不同的aggregators分别是:
1)Mean aggregator: 该策略是将邻居节点与目标节点特征向量的值取平均

2)LSTM aggregator: 利用LSTM来聚合邻居节点的信息。
3)Pooling aggregator: 在使用pooling聚合器的时候,每个邻居节点的特征逐一的经过一个全连接层,从而进行池化操作

这里的max是一个element-wise的max.
2. 代码解析
- 代码参考地址:graphSAGE-pytorch
- 导入所需的库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os,sys
import argparse
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import random
import math
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
from collections import defaultdict
2.1 加载数据
- 本代码使用的数据cora共包含两个文件,分别是cora_content和cora_cite. 数据详细描述可参考链接:Cora数据集描述
class DataCenter(object):
"""加载数据集
Parameter:
file_paths:{数据文件存放地址1,数据文件存放地址2}
"""
def __init__(self,file_paths):
"""file_paths:{name:root,...,}"""
super(DataCenter,self).__init__()
self.file_paths = file_paths
def load_Dataset(self,dataset='cora'):
"""读取存放在指定路径的数据集"""
feat_list = [] # 用于存放每个节点特征向量的列表
label_list = [] # 用于存放每个节点对应类别的列表
node_map = {} # 将节点进行重新编码
label_map = {} # 将label映射为数字
if dataset == 'cora':
content = self.file_paths['cora_content'] # 获取cora_content的地址
cite = self.file_paths['cora_cite'] # 获取cora_cite的地址
with open(content) as f1:
for i,each_sample in enumerate(f1.readlines()): # 遍历每个样本的特征
sample_clean = each_sample.strip().split()
# 提取每个样本的特征,其中第一个元素和最后一个元素是样本名称和对应的标签
feat_list.append(sample_clean[1:-1])
# 把节点名称映射为节点编号
node_map[sample_clean[0]]=i
label = sample_clean[-1]
if label not in label_map.keys():
# 把label转化为数字
label_map[label] = len(label_map)
label_list.append(label_map[label])
feat_list = np.asarray(feat_list,dtype=np.float64)
label_list = np.asarray(label_list,dtype=np.int64)
# 获得每个节点的邻居{v0:[v0的邻居集合],v1:[v1的邻居集合]}
adj_lists = defaultdict(set)
with open(cite) as f2:
for j,each_pair in enumerate(f2.readlines()):
pair = each_pair.strip().split()
assert len(pair) == 2
adj_lists[node_map[pair[0]]].add(node_map[pair[1]])
adj_lists[node_map[pair[1]]].add(node_map[pair[0]])
assert len(feat_list) == len(label_list) == len(adj_lists)
train_index,test_index,val_index = self._split_data(feat_list.shape[0])
# 使用getattr()可以获得数据
setattr(self,dataset+'_test',test_index)
setattr(self,dataset+'_val',val_index)
setattr(self,dataset+'_train',train_index)
setattr(self,dataset+'_feats',feat_list)
setattr(self,dataset+'_labels',label_list)
setattr(self,dataset+'_adj_lists',adj_lists)
def _split_data(self,number_of_nodes,test_split=3,val_split=6):
"""获得训练集、验证集和测试集"""
# 打乱顺序
rand_indices = np.random.permutation(number_of_nodes)
test_size = number_of_nodes // test_split
val_size = number_of_nodes // val_split
test_index = rand_indices[:test_size]
val_index = rand_indices[test_size:test_size+val_size]
train_index = rand_indices[test_size+val_size:]
return train_index,test_index,val_index
2.2 Unsupervised Loss
GraphSAGE定义的Loss函数如下所示,
J
G
(
z
u
)
=
−
l
o
g
(
σ
(
z
u
T
z
v
)
)
−
Q
E
v
n
P
n
(
v
)
l
o
g
(
σ
(
−
z
u
T
z
v
n
)
)
J_G(z_u)=-log(\sigma(z_u^Tz_v))-QE_{v_n ~ P_n(v)}log(\sigma(-z_u^Tz_{v_n}))
JG(zu)=−log(σ(zuTzv))−QEvn Pn(v)log(σ(−zuTzvn))
其中,
Q
Q
Q为负样本数量,前一项是根据正样本计算的Loss,后一项是根据负样本计算的Loss.
class UnsupervisedLoss(object):
"""docstring for UnsupervisedLoss"""
def __init__(self, adj_lists, train_nodes, device):
"""初始化参数"""
super(UnsupervisedLoss, self).__init__()
self.Q = 10 # 负样本的数量
self.N_WALKS = 6 # 每个节点随机游走的次数
self.WALK_LEN = 1 # 每次随机游走的步长
self.N_WALK_LEN = 5 # 每次负样本随机游走几个节点
self.MARGIN = 3
self.adj_lists = adj_lists #{v0:[v0的邻居集合],v1:[v1的邻居集合],...,vn:[vn的邻居集合]}
self.train_nodes = train_nodes # 训练节点
self.device = device # cpu or gpu
self.target_nodes = None
self.positive_pairs = [] # 存放正例样本 [(v0,v0邻居中采样到的正例节点),....,]
self.negtive_pairs = [] # 存放负例样本 [(v0,v0邻居中采样到的负例节点),....,]
self.node_positive_pairs = {} # {v0:[(v0,从v0开始随机游走采样到的正例节点),(v0,从v0开始随机游走采样到的正例节点)],...,vn:[(vn,从vn开始随机游走采样到的正例节点)]}
self.node_negtive_pairs = {} # {v0:[(v0,从v0开始随机游走采样到的负例节点),(v0,从v0开始随机游走采样到的负例节点)],...,vn:[(vn,从vn开始随机游走采样到的负例节点)]}
self.unique_nodes_batch = [] # 一个batch所有会用到的节点及其邻居节点
def get_loss_sage(self, embeddings, nodes):
"""根据论文里的公式计算损失函数"""
assert len(embeddings) == len(self.unique_nodes_batch) #判断是不是每个节点都有了embeddings
assert False not in [nodes[i]==self.unique_nodes_batch[i] for i in range(len(nodes))] # 判断目标节点集和unique集里的节点是否1一一对应
node2index = {n:i for i,n in enumerate(self.unique_nodes_batch)} # 把节点重新编码
nodes_score = []
assert len(self.node_positive_pairs) == len(self.node_negtive_pairs) # 确定正例节点对和负例节点对的数量是否相同
for node in self.node_positive_pairs: # 遍历所有节点
pps = self.node_positive_pairs[node] # 获得对应的正例 [(v0,v0正例样本1),(v0,v0正例样本2),...,(v0,v0正例样本n)]
nps = self.node_negtive_pairs[node] # 获得每个节点对应的负例 [(v0,v0负例样本1),(v0,v0负例样本2),...,(v0,v0负例样本n)]
if len(pps) == 0 or len(nps) == 0: # 判断是否都有正例和负例
continue
# Q * Exception(negative score)计算负例样本的Loss,即Loss函数的后一项
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*nps)] # [[源节点,...,源节点],[采样得到的负节点1,...,采样得到的负节点n]]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]] # 获得源节点的编号
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]] # 负样本节点的编号
neg_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs]) # 计算余弦相似性
neg_score = self.Q*torch.mean(torch.log(torch.sigmoid(-neg_score)), 0) # 计算损失的后一项
#print(neg_score)
# multiple positive score 计算正列样本的Loss,即Loss函数的前一项
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*pps)]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]]
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]]
pos_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs])
pos_score = torch.log(torch.sigmoid(pos_score)) # 计算损失的前一项
#print(pos_score)
nodes_score.append(torch.mean(- pos_score - neg_score).view(1,-1)) # 把每个节点的损失加入到列表中
loss = torch.mean(torch.cat(nodes_score, 0)) # 求平均
return loss
def get_loss_margin(self, embeddings, nodes):
assert len(embeddings) == len(self.unique_nodes_batch)
assert False not in [nodes[i]==self.unique_nodes_batch[i] for i in range(len(nodes))]
node2index = {n:i for i,n in enumerate(self.unique_nodes_batch)}
nodes_score = []
assert len(self.node_positive_pairs) == len(self.node_negtive_pairs)
for node in self.node_positive_pairs:
pps = self.node_positive_pairs[node]
nps = self.node_negtive_pairs[node]
if len(pps) == 0 or len(nps) == 0:
continue
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*pps)]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]]
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]]
pos_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs])
pos_score, _ = torch.min(torch.log(torch.sigmoid(pos_score)), 0)
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*nps)]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]]
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]]
neg_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs])
neg_score, _ = torch.max(torch.log(torch.sigmoid(neg_score)), 0)
nodes_score.append(torch.max(torch.tensor(0.0).to(self.device), neg_score-pos_score+self.MARGIN).view(1,-1))
# nodes_score.append((-pos_score - neg_score).view(1,-1))
loss = torch.mean(torch.cat(nodes_score, 0),0)
# loss = -torch.log(torch.sigmoid(pos_score))-4*torch.log(torch.sigmoid(-neg_score))
return loss
def extend_nodes(self, nodes, num_neg=6):
"""获得目标节点集的正样本和负样本,输出这些节点的集合"""
self.positive_pairs = []
self.node_positive_pairs = {}
self.negtive_pairs = []
self.node_negtive_pairs = {}
self.target_nodes = nodes
self.get_positive_nodes(nodes)
# print(self.positive_pairs)
self.get_negtive_nodes(nodes, num_neg)
# print(self.negtive_pairs)
self.unique_nodes_batch = list(set([i for x in self.positive_pairs for i in x]) | set([i for x in self.negtive_pairs for i in x]))
assert set(self.target_nodes) < set(self.unique_nodes_batch)
return self.unique_nodes_batch
def get_positive_nodes(self, nodes):
return self._run_random_walks(nodes) # 通过随机游走获得正列样本
def get_negtive_nodes(self, nodes, num_neg):
"""
生成负样本,也就是让目标节点与目标节点相隔很远的节点组成一个负例
"""
for node in nodes: # 遍历每个节点
neighbors = set([node])
frontier = set([node])
for i in range(self.N_WALK_LEN):
current = set()
for outer in frontier:
current |= self.adj_lists[int(outer)] #获取frontier中所有的邻居节点
frontier = current - neighbors #去除源节点
neighbors |= current # 源节点+邻居节点
far_nodes = set(self.train_nodes) - neighbors # 减去train_nodes里源节点及其一阶邻居
neg_samples = random.sample(far_nodes, num_neg) if num_neg < len(far_nodes) else far_nodes # 从二阶邻居开始采样
self.negtive_pairs.extend([(node, neg_node) for neg_node in neg_samples])
self.node_negtive_pairs[node] = [(node, neg_node) for neg_node in neg_samples]
return self.negtive_pairs
def _run_random_walks(self, nodes):
for node in nodes: # 遍历每个节点
if len(self.adj_lists[int(node)]) == 0: # 若该节点没有邻居节点则跳过
continue
cur_pairs = [] # 创建一个
for i in range(self.N_WALKS): # 每个节点会有N_WALKS次的随机游走
curr_node = node #
for j in range(self.WALK_LEN): # 每次随机游走走WALK_LEN的长度
neighs = self.adj_lists[int(curr_node)]
next_node = random.choice(list(neighs))
# self co-occurrences are useless
if next_node != node and next_node in self.train_nodes:
self.positive_pairs.append((node,next_node))
cur_pairs.append((node,next_node))
curr_node = next_node
self.node_positive_pairs[node] = cur_pairs
return self.positive_pairs
2.3 Models
- Classification model
class Classification(nn.Module):
"""一个最简单的一层分类模型
Parameters:
input_size:输入维度
num_classes:类别数量
return:
logists:最大概率对应的标签
"""
def __init__(self,input_size,num_classes):
super(Classification,self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_size,num_classes) # 定义一个input_size*num_classes的线性层
self.init_params() # 初始化权重参数
def init_params(self):
for param in self.parameters():
if len(param.size()) == 2: # 如果参数是矩阵的话就重新初始化
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(param)
def forward(self,x):
logists = torch.log_softmax(self.fc1(x),1) # 利用log_softmax来获得最终输出的类别
return logists
- GraphSAGE
class SageLayer(nn.Module):
"""
一层SageLayer
"""
def __init__(self, input_size, out_size, gcn=False):
super(SageLayer, self).__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.out_size = out_size
self.gcn = gcn
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_size, self.input_size if self.gcn else 2 * self.input_size)) #初始化权重参数w*input.T
self.init_params() # 调整权重参数分布
def init_params(self):
for param in self.parameters():
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(param)
def forward(self, self_feats, aggregate_feats, neighs=None):
"""
Parameters:
self_feats:源节点的特征向量
aggregate_feats:聚合后的邻居节点特征
"""
if not self.gcn: # 如果不是gcn的话就要进行concatenate
combined = torch.cat([self_feats, aggregate_feats], dim=1)
else:
combined = aggregate_feats
combined = F.relu(self.weight.mm(combined.t())).t()
return combined
class GraphSage(nn.Module):
"""定义一个GraphSage模型"""
def __init__(self, num_layers, input_size, out_size, raw_features, adj_lists, device, gcn=False, agg_func='MEAN'):
super(GraphSage, self).__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.out_size = out_size
self.num_layers = num_layers # Graphsage的层数
self.gcn = gcn
self.device = device
self.agg_func = agg_func
self.raw_features = raw_features
self.adj_lists = adj_lists
# 定义每一层的输入和输出
for index in range(1, num_layers+1):
layer_size = out_size if index != 1 else input_size
setattr(self, 'sage_layer'+str(index), SageLayer(layer_size, out_size, gcn=self.gcn))#除了第1层的输入为input_size,其余层的输入和输出均为outsize
def forward(self, nodes_batch):
"""
为一批节点生成嵌入表示
Parameters:
nodes_batch:目标批次的节点
"""
lower_layer_nodes = list(nodes_batch) # 初始化第一层节点
nodes_batch_layers = [(lower_layer_nodes,)] # 存放每一层的节点信息
for i in range(self.num_layers):
lower_samp_neighs, lower_layer_nodes_dict, lower_layer_nodes= self._get_unique_neighs_list(lower_layer_nodes) # 根据当前层节点获得下一层节点
nodes_batch_layers.insert(0, (lower_layer_nodes, lower_samp_neighs, lower_layer_nodes_dict))
assert len(nodes_batch_layers) == self.num_layers + 1
pre_hidden_embs = self.raw_features # 初始化h0
for index in range(1, self.num_layers+1):
nb = nodes_batch_layers[index][0] #所有邻居节点
pre_neighs = nodes_batch_layers[index-1] # 上一层的邻居节点
aggregate_feats = self.aggregate(nb, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs)
sage_layer = getattr(self, 'sage_layer'+str(index))
if index > 1:
nb = self._nodes_map(nb, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs)
# self.dc.logger.info('sage_layer.')
cur_hidden_embs = sage_layer(self_feats=pre_hidden_embs[nb],
aggregate_feats=aggregate_feats)
pre_hidden_embs = cur_hidden_embs
return pre_hidden_embs
def _nodes_map(self, nodes, hidden_embs, neighs):
layer_nodes, samp_neighs, layer_nodes_dict = neighs
assert len(samp_neighs) == len(nodes)
index = [layer_nodes_dict[x] for x in nodes]
return index
def _get_unique_neighs_list(self, nodes, num_sample=10):
_set = set
to_neighs = [self.adj_lists[int(node)] for node in nodes] # 获取目标节点集的所有邻居节点[[v0的邻居],[v1的邻居],[v2的邻居]]
if not num_sample is None: # 如果num_sample为实数的话
_sample = random.sample
samp_neighs = [_set(_sample(to_neigh, num_sample)) if len(to_neigh) >= num_sample else to_neigh for to_neigh in to_neighs] # [set(随机采样的邻居集合),set(),set()]
# 遍历所有邻居集合如果邻居节点数>=num_sample,就从邻居节点集中随机采样num_sample个邻居节点,否则直接把邻居节点集放进去
else:
samp_neighs = to_neighs
samp_neighs = [samp_neigh | set([nodes[i]]) for i, samp_neigh in enumerate(samp_neighs)] # 把源节点也放进去
_unique_nodes_list = list(set.union(*samp_neighs)) #展平
i = list(range(len(_unique_nodes_list))) # 重新编号
unique_nodes = dict(list(zip(_unique_nodes_list, i)))
return samp_neighs, unique_nodes, _unique_nodes_list
def aggregate(self, nodes, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs, num_sample=10):
"""聚合邻居节点信息
Parameters:
nodes:从最外层开始的节点集合
pre_hidden_embs:上一层的节点嵌入
pre_neighs:上一层的节点
"""
unique_nodes_list, samp_neighs, unique_nodes = pre_neighs # 上一层的源节点,...,....,
assert len(nodes) == len(samp_neighs)
indicator = [(nodes[i] in samp_neighs[i]) for i in range(len(samp_neighs))] # 判断每个节点是否出现在邻居节点中
assert (False not in indicator)
if not self.gcn:
# 如果不适用gcn就要把源节点去除
samp_neighs = [(samp_neighs[i]-set([nodes[i]])) for i in range(len(samp_neighs))]
if len(pre_hidden_embs) == len(unique_nodes):
embed_matrix = pre_hidden_embs
else:
embed_matrix = pre_hidden_embs[torch.LongTensor(unique_nodes_list)]
# self.dc.logger.info('3')
mask = torch.zeros(len(samp_neighs), len(unique_nodes))
column_indices = [unique_nodes[n] for samp_neigh in samp_neighs for n in samp_neigh]
row_indices = [i for i in range(len(samp_neighs)) for j in range(len(samp_neighs[i]))]
mask[row_indices, column_indices] = 1 # 每个源节点为一行,一行元素中1对应的就是邻居节点的位置
if self.agg_func == 'MEAN':
num_neigh = mask.sum(1, keepdim=True) # 计算每个源节点有多少个邻居节点
mask = mask.div(num_neigh).to(embed_matrix.device) #
aggregate_feats = mask.mm(embed_matrix)
elif self.agg_func == 'MAX':
# print(mask)
indexs = [x.nonzero() for x in mask==1]
aggregate_feats = []
for feat in [embed_matrix[x.squeeze()] for x in indexs]:
if len(feat.size()) == 1:
aggregate_feats.append(feat.view(1, -1))
else:
aggregate_feats.append(torch.max(feat,0)[0].view(1, -1))
aggregate_feats = torch.cat(aggregate_feats, 0)
return aggregate_feats
2.4 评估与模型使用
def evaluate(dataCenter, ds, graphSage, classification, device, max_vali_f1, name, cur_epoch):
"""
测试模型的性能
Parameters:
datacenter:创建好的datacenter对像
ds:数据集的名称
graphSage:训练好的graphSage对像
classification:训练好的classificator
"""
test_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_test') # 获得测试集
val_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_val') # 获得验证集
labels = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels') # 获得标签
models = [graphSage, classification]
params = [] # 将两个模型的参数存入一个列表中
for model in models:
for param in model.parameters():
if param.requires_grad:
param.requires_grad = False
params.append(param)
embs = graphSage(val_nodes)
logists = classification(embs)
_, predicts = torch.max(logists, 1)
labels_val = labels[val_nodes]
assert len(labels_val) == len(predicts)
comps = zip(labels_val, predicts.data)
vali_f1 = f1_score(labels_val, predicts.cpu().data, average="micro")
print("Validation F1:", vali_f1)
if vali_f1 > max_vali_f1:
max_vali_f1 = vali_f1
embs = graphSage(test_nodes)
logists = classification(embs)
_, predicts = torch.max(logists, 1)
labels_test = labels[test_nodes]
assert len(labels_test) == len(predicts)
comps = zip(labels_test, predicts.data)
test_f1 = f1_score(labels_test, predicts.cpu().data, average="micro")
print("Test F1:", test_f1)
for param in params:
param.requires_grad = True
torch.save(models, './model_best_{}_ep{}_{:.4f}.torch'.format(name, cur_epoch, test_f1))
for param in params:
param.requires_grad = True
return max_vali_f1
def get_gnn_embeddings(gnn_model, dataCenter, ds):
"""使用GraphSage获得节点的嵌入表示"""
print('Loading embeddings from trained GraphSAGE model.')
features = np.zeros((len(getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels')), gnn_model.out_size))
nodes = np.arange(len(getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels'))).tolist()
b_sz = 500
batches = math.ceil(len(nodes) / b_sz)
embs = []
for index in range(batches):
nodes_batch = nodes[index*b_sz:(index+1)*b_sz]
embs_batch = gnn_model(nodes_batch)
assert len(embs_batch) == len(nodes_batch)
embs.append(embs_batch)
# if ((index+1)*b_sz) % 10000 == 0:
# print(f'Dealed Nodes [{(index+1)*b_sz}/{len(nodes)}]')
assert len(embs) == batches
embs = torch.cat(embs, 0)
assert len(embs) == len(nodes)
print('Embeddings loaded.')
return embs.detach()
def train_classification(dataCenter, graphSage, classification, ds, device, max_vali_f1, name, epochs=800):
"""训练分类器"""
print('Training Classification ...')
c_optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(classification.parameters(), lr=0.5)
# train classification, detached from the current graph
#classification.init_params()
b_sz = 50
train_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_train')
labels = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels')
features = get_gnn_embeddings(graphSage, dataCenter, ds)
for epoch in range(epochs):
train_nodes = shuffle(train_nodes)
batches = math.ceil(len(train_nodes) / b_sz)
visited_nodes = set()
for index in range(batches):
nodes_batch = train_nodes[index*b_sz:(index+1)*b_sz]
visited_nodes |= set(nodes_batch)
labels_batch = labels[nodes_batch]
embs_batch = features[nodes_batch]
logists = classification(embs_batch)
loss = -torch.sum(logists[range(logists.size(0)), labels_batch], 0)
loss /= len(nodes_batch)
# print('Epoch [{}/{}], Step [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}, Dealed Nodes [{}/{}] '.format(epoch+1, epochs, index, batches, loss.item(), len(visited_nodes), len(train_nodes)))
loss.backward()
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(classification.parameters(), 5)
c_optimizer.step()
c_optimizer.zero_grad()
max_vali_f1 = evaluate(dataCenter, ds, graphSage, classification, device, max_vali_f1, name, epoch)
return classification, max_vali_f1
def apply_model(dataCenter, ds, graphSage, classification, unsupervised_loss, b_sz, unsup_loss, device, learn_method):
test_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_test')
val_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_val')
train_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_train')
labels = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels')
if unsup_loss == 'margin':
num_neg = 6
elif unsup_loss == 'normal':
num_neg = 100
else:
print("unsup_loss can be only 'margin' or 'normal'.")
sys.exit(1)
train_nodes = shuffle(train_nodes)
models = [graphSage, classification]
params = []
for model in models:
for param in model.parameters():
if param.requires_grad:
params.append(param)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=0.7)
optimizer.zero_grad()
for model in models:
model.zero_grad()
batches = math.ceil(len(train_nodes) / b_sz)
visited_nodes = set()
for index in range(batches):
nodes_batch = train_nodes[index*b_sz:(index+1)*b_sz]
# extend nodes batch for unspervised learning
# no conflicts with supervised learning
nodes_batch = np.asarray(list(unsupervised_loss.extend_nodes(nodes_batch, num_neg=num_neg)))
visited_nodes |= set(nodes_batch)
# get ground-truth for the nodes batch
labels_batch = labels[nodes_batch]
# feed nodes batch to the graphSAGE
# returning the nodes embeddings
embs_batch = graphSage(nodes_batch)
if learn_method == 'sup':
# superivsed learning
logists = classification(embs_batch)
loss_sup = -torch.sum(logists[range(logists.size(0)), labels_batch], 0)
loss_sup /= len(nodes_batch)
loss = loss_sup
elif learn_method == 'plus_unsup':
# superivsed learning
logists = classification(embs_batch)
loss_sup = -torch.sum(logists[range(logists.size(0)), labels_batch], 0)
loss_sup /= len(nodes_batch)
# unsuperivsed learning
if unsup_loss == 'margin':
loss_net = unsupervised_loss.get_loss_margin(embs_batch, nodes_batch)
elif unsup_loss == 'normal':
loss_net = unsupervised_loss.get_loss_sage(embs_batch, nodes_batch)
loss = loss_sup + loss_net
else:
if unsup_loss == 'margin':
loss_net = unsupervised_loss.get_loss_margin(embs_batch, nodes_batch)
elif unsup_loss == 'normal':
loss_net = unsupervised_loss.get_loss_sage(embs_batch, nodes_batch)
loss = loss_net
print('Step [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}, Dealed Nodes [{}/{}] '.format(index+1, batches, loss.item(), len(visited_nodes), len(train_nodes)))
loss.backward()
for model in models:
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), 5)
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
for model in models:
model.zero_grad()
return graphSage, classification
2.5 Main
file_paths = {'cora_content':'./cora.content','cora_cite':'./cora.cites'}
datacenter = DataCenter(file_paths)
datacenter.load_Dataset()
feature_data = torch.FloatTensor(getattr(datacenter, 'cora'+'_feats'))
label_data = torch.from_numpy(getattr(datacenter,'cora'+'_labels')).long()
adj_lists = getattr(datacenter,'cora'+'_adj_lists')
random.seed(824)
np.random.seed(824)
torch.manual_seed(824)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(824)
learn_method = 'sup'
ds = 'cora'
epochs = 50
max_vali_f1=0
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
graphSage = GraphSage(2, feature_data.size(1), 128, feature_data, getattr(datacenter, ds+'_adj_lists'), device, gcn='store_true', agg_func='MEAN')
num_labels = len(set(getattr(datacenter, ds+'_labels')))
classification = Classification(128, num_labels)
unsupervised_loss = UnsupervisedLoss(getattr(datacenter, ds+'_adj_lists'), getattr(datacenter, ds+'_train'), device)
if learn_method == 'sup':
print('GraphSage with Supervised Learning')
elif learn_method == 'plus_unsup':
print('GraphSage with Supervised Learning plus Net Unsupervised Learning')
else:
print('GraphSage with Net Unsupervised Learning')
for epoch in range(epochs):
print('----------------------EPOCH %d-----------------------' % epoch)
graphSage, classification = apply_model(datacenter, ds, graphSage, classification, unsupervised_loss, 20, 'normal', device, learn_method)
if (epoch+1) % 2 == 0 and learn_method == 'unsup':
classification, max_vali_f1 = train_classification(datacenter, graphSage, classification, ds, device,max_vali_f1, 'debug')
if learn_method != 'unsup':
max_vali_f1 = evaluate(datacenter, ds, graphSage, classification, device, max_vali_f1 , 'debug', epoch)
- 输出结果如下:

参考资料
[1] Hamilton W L, Ying R, Leskovec J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.02216, 2017.
[2] https://github.com/twjiang/graphSAGE-pytorch
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)