二、python中Pandas数据框操作及数据提取
二、Pandas数据框操作及数据提取#导包import pandas as pdimport numpy as np数据框行列操作1.1 创建DataFramedata = {"col1":['Python', 'C', 'Java', 'R', 'SQL', 'PHP', 'Python', 'Java', 'C', 'Python'],"col2":[6, 2, 6, 4, 2, 5, 8,
二、Pandas数据框操作及数据提取
#导包
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
- 数据框行列操作
1.1 创建DataFrame
data = {"col1":['Python', 'C', 'Java', 'R', 'SQL', 'PHP', 'Python', 'Java', 'C', 'Python'],
"col2":[6, 2, 6, 4, 2, 5, 8, 10, 3, 4],
"col3":[4, 2, 6, 2, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 6]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
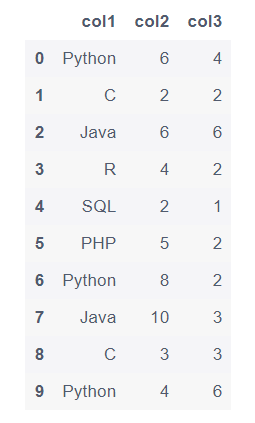
1.2 设置索引
df['new_index'] = range(1,11)
df.set_index('new_index')

1.3 重置索引(行号)
df.reset_index(drop=True,inplace = True) # drop = True:原有索引就不会成为新的列
df

1.4 更改列名
#方法一:直接法
df.columns = ['grammer', 'score', 'cycle', 'id']
#方法二:(使用rename()函数:修改指定修改某列或某几列名字)
df.rename(columns={'col1':'grammer', 'col2':'score', 'col3':'cycle','new_index':'id'}, inplace=True)
df.head()

1.5 调整列顺序
(1) 将所有列倒序排列
#方法一:
df.iloc[:, ::-1]
#方法二
df.iloc[:, [-1,-2,-3,-4]]

(2) 交换两列位置
temp = df['grammer']
df.drop(labels=['grammer'], axis=1, inplace=True)
df.insert(1, 'grammer', temp)
df
(3) 更改全部列顺序
order = df.columns[[0, 3, 1, 2]] # 或者order = ['xx', 'xx',...] 具体列名
df = df[order]
df
1.6 删除行列
(1) 删除id这一列
# 法一:
del df['id']
# 法二:
df['id'] = range(1,11)
df.drop('id',axis=1, inplace=True) #columns=['xxx']
(2) 添加一行grammer='css’数据,并删除该行
df.drop(labels=[df[df['grammer']=='css'].index[0]],axis=0,inplace=True)
df
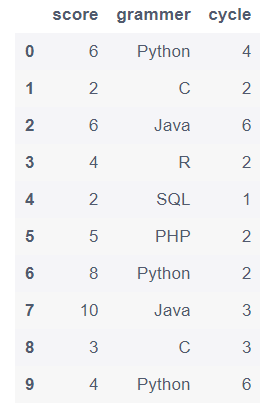
1.7 将grammer列和score列合并成新的一列
df['new_col'] = df['grammer'] + df['score'].map(str) # score为int类型,需转换为字符串类型;
df

1.8 将数据按行的方式逆序输出
df.iloc[::-1, :]
# [::-1]表示步长为-1, 从后往前倒序输出
- 数据读取与保存
2.1 读取excel文件
excel = pd.read_excel('/home/mw/input/pandas1206855/pandas120.xlsx')
excel.head()

2.2 读取csv文件
csv = pd.read_csv('/home/mw/input/pandas_exercise/pandas_exercise/exercise_data/drinks.csv')
csv.head()

2.3 读取tsv文件
tsv = pd.read_csv('/home/mw/input/pandas_exercise/pandas_exercise/exercise_data/chipotle.tsv', sep = '\t')
tsv.head()

2.4 dataframe保存为csv文件
df.to_csv('course.csv')
2.5 读取时设置显示行列的参数:pd.set_option()
#(1) 显示所有列
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 2) #最多显示5列
#(2) 显示所有行
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 10)#最多显示10行
#(3) 显示小数位数
pd.set_option('display.float_format',lambda x: '%.2f'%x) #两位
#(4) 显示宽度
pd.set_option('display.width', 100)
#(5) 设置小数点后的位数
pd.set_option('precision', 1)
#(6) 是否换行显示
pd.set_option('expand_frame_repr', False)
# True就是可以换行显示。设置成False的时候不允许换行
- 提取指定行列的数据
# 读取pandas120数据文件
df = pd.read_excel('/home/mw/input/pandas1206855/pandas120.xlsx')
df.head()
3.1 提取第32行数据
# 方法一:
df.loc[32]
# 方法二:
df.iloc[32,:] # df.iloc[32] 也可
3.2 提取education这一列数据
df['education']
3.3 提取后两列(education, salary)数据
# 方法一:
df[['education', 'salary']]
# 方法二:
df.iloc[:, 1:]
3.4 提取第一列位置在1,10,15上的值
# 方法一:
df.iloc[[1,10,15], 0]
# 方法二:
df['createTime'][[1,10,15]]
# 方法三:
df['createTime'].take([1,10,15])
- 提取重复值所在的行列数据
4.1 判断createTime列数据是否重复
df.createTime.duplicated()
4.2 判断数据框中所有行是否存在重复
df.duplicated()
4.3 判断education列和salary列数据是否重复(多列组合查询)
df.duplicated(subset = ['education','salary'])
4.4 判断重复索引所在行列数据
df.index.duplicated()
- 按指定条件提取元素值
这里为了运行后续代码,通过random函数随机添加一列数据;
import random
df['value'] = [random.randint(1,100) for i in range(len(df))]
df.head()
5.1 提取value列元素值大于90的行
df[df['value'] > 90]
5.3 提取某列最大值所在的行
df[df['value'] == df['value'].max()]
5.4 提取value和value1之和大于150的最后三行
df[(df['value'] + df['value1']) > 150].tail(3)
- 提取含空值的行列
为了演示代码,这里设置一些值;
df.loc[[2,10,45,87], 'value'] = np.nan
df.loc[[19,30,55,97,114], 'value1'] = np.nan
df.loc[[24,52,67,120], 'education'] = 111
df.loc[[8,26,84], 'salary'] = '--'
6.1 提取value列含有空值的行
df[df['value'].isnull()]

6.2 提取每列缺失值的具体行数
for columname in df.columns: #遍历每一列
if df[columname].count() != len(df): #判断缺失行条件:所在列的值数等于总数据的长度
#将存在缺失值的行的索引转换成列表储存
loc = df[columname][df[columname].isnull().values == True].index.tolist()
print('列名:"{}",第{}行位置有缺失值'.format(columname, loc))
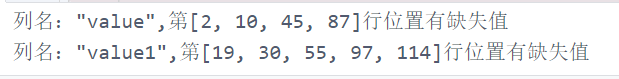
7. 提取某列不是数值或(包含)字符串的行
7.1 提取education列数值类型不是字符串的行
temp = pd.DataFrame()
for i in range(len(df)):
if type(df['education'][i]) != str: #df['xxx'][i]或写成df.iloc[i,j]
temp = temp.append(df.loc[i])
temp

7.3 提取education列值为’硕士’的行`
# 方法一:
df[df['education'] == '硕士']
# 方法二:
results = df['education'].str.contains('硕士')
results.fillna(value=False, inplace=True)
df[results]
- 其他提取操作
8.1 提取学历为本科和硕士的数据,只显示学历和薪资两列
# 方法一:isin()
df[df['education'].isin(['本科', '硕士'])] [['education', 'salary']]
# 方法二:loc提取
df.loc[df['education'].isin(['本科', '硕士']), ['education', 'salary']]
8.2 提取salary列以’25k’开头的行
# 方法一:match函数
df[df['salary'].str.match('25k')]
# 方法二:startswith函数
df[df['salary'].str.startswith('25k')]
8.3 提取value列中不在value1列出现的数字
df['value'][~df['value'].isin(df['value1'])] #~取反
8.4 提取value列和value1列出现频率最高的数字
# 先将两列使用append()按行合并,再用计数函数:
temp = df['value'].append(df['value1'])
temp.value_counts(ascending=False)#不加index,返回的是一个Series
temp.value_counts(ascending=False).index[:5] #返回一个数组
8.5 提取value列中可以整除10的数字位置
#方法一:
df[df['value'] % 10 == 0].index
#方法二:np.argwhere
np.argwhere(np.array(df['value'] % 10 == 0))
作业练习:
#读取pandas120数据文件
df = pd.read_excel('/home/mw/input/pandas1206855/pandas120.xlsx')
df.head()
#1. 提取学历为本科,工资在25k-35k的数据
df1 = df[(df['salary']=='25k-35k') & (df['education']=='本科')]
#2. 提取salary列中以'40k'结尾的数据
df2 = df[df['salary'].str.endswith('40k')]
#3. 提取薪资区间中最低薪资与最高薪资的平均值大于30k的行,只需提取原始字段('createTime', 'education', 'salary')即可
result = []
import re
for x in df['salary']:
result.append((int(re.split('[k-]', x)[0])+int(re.split('[k-]', x)[2]))/2)
df['result'] = result
df3 = df[df['result']>30][['createTime','education','salary']]
len(df3)
#4. 将以上三题提取出来的行按照相同列进行合并,汇总到一个数据框中;
answer_2 = pd.concat([df1, df2, df3], axis=0)
#5. 将三列数据合并成一列,并设置列名为answer,最后保留id(数据行数、answer)
data = pd.concat([answer_2.iloc[:,0],answer_2.iloc[:,1],answer_2.iloc[:,2]])
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['answer'])
df['id'] = range(len(df))
df = df[['id', 'answer']]
# 保存文件到本地
df.to_csv('answer_2.csv', index=False, encoding='utf-8-sig')
学习资料:
https://www.heywhale.com/home/activity
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)