Numpy中创建数组的n种方式,你都了解吗?
1、使用empty方法创建数组该方式可以创建一个空数组,dtype可以指定随机数的类型,否则随机采用一种类型生成随机数。import numpy as npdt = np.numpy([2, 2], dtype=int)2、使用array创建数组使用array方法可以基于Python列表创建数组,在不设置dtype的情况下,从列表中自动推断数据类型。import numpy as npdt = n
·
1、使用empty方法创建数组
该方式可以创建一个空数组,dtype可以指定随机数的类型,否则随机采用一种类型生成随机数。
import numpy as np
dt = np.numpy([2, 2], dtype=int)

2、使用array创建数组
使用array方法可以基于Python列表创建数组,在不设置dtype的情况下,从列表中自动推断数据类型。
import numpy as np
dt = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)
dt = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype='f8') # 64位浮点数
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)

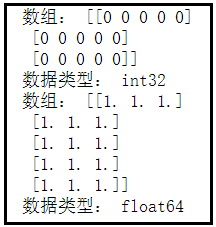
3、使用zeros/ones创建数组
调用zeros/ones方法会创建一个全为‘0’/‘1’值的数组,通常在数组元素位置,大小一致的情况下来生成临时数组。‘0’/‘1’充当占位符。
import numpy as np
dt = np.zeros([3, 5], dtype=int)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)
dt = np.ones([5, 3], dtype=float)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)
4、使用arange创建数组
使用arange方法可以基于一个数据范围来创建数组。
import numpy as np
dt = np.arange(10, 30, 5)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)

5、使用linspace创建数组
linspace是基于一个范围来构造数组,参数num是开始值和结束值之间需要创建多少个数值。
retstep会改变计算的输出,返回一个元组,而元组的两个元素分别是需要生成的数组和数组的步差值。
import numpy as np
dt = np.linspace(20, 30, num=5)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)
dt = np.linspace(20, 30, num=5, endpoint=False)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)
dt = np.linspace(20, 30, num=5, retstep=True)
print('元组:', dt)

6、使用numpy.random.rand创建数组
很多情况下手动创建的数组往往不能满足业务需求,因此需要创建随机数组。
import numpy as np
dt = np.random.rand(10)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)

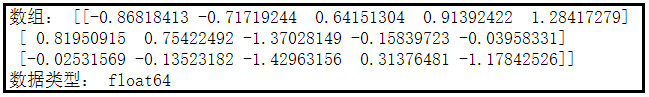
7、使用numpy.random.randn创建数组
numpy.random.randn方法也是产生随机数组的一种方式,并且它能产生符合正态分布的随机数。
import numpy as np
dt = np.random.randn(3, 5)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)
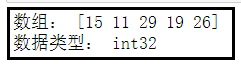
8、使用numpy.random.randint创建数组
在10和30之间产生随机数,并从中取5个数值来构建数组。
import numpy as np
dt = np.random.randint(10, 30, 5)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)
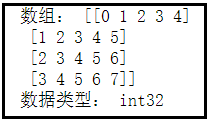
9、使用fromfunction创建数组
fromfunction方法可以通过一个函数规则来创建数组。该方法中shape参数制定了创建数组的规则,shape=(4,5),最终创建的结果就是4行5列的二维数组。
import numpy as np
dt = np.fromfunction(lambda i, j:i + j, (4, 5), dtype=int)
print('数组:', dt)
print('数据类型:', dt.dtype)
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容






所有评论(0)