yolov5输出检测到的目标坐标信息/位置
找到detect.py,在大概113行,找到plot_one_box# Write resultsfor *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):if save_txt:# Write to filexywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(
·
找到detect.py,在大概113行,找到plot_one_box
# Write results
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
if save_txt: # Write to file
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywh
with open(txt_path + '.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(('%g ' * 5 + '\n') % (cls, *xywh)) # label format
if save_img or view_img: # Add bbox to image
label = '%s %.2f' % (names[int(cls)], conf)
plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=3)
ctr+鼠标点击,进入general.py,并自动定位到plot_one_box函数,修改函数为
def plot_one_box(x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=None):
# Plots one bounding box on image img
tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
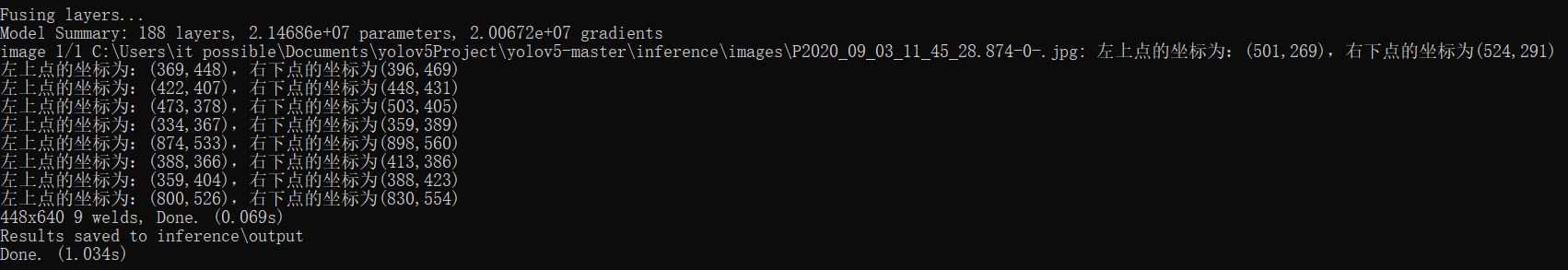
print("左上点的坐标为:(" + str(c1[0]) + "," + str(c1[1]) + "),右下点的坐标为(" + str(c2[0]) + "," + str(c2[1]) + ")")
即可输出目标坐标信息了
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容









所有评论(0)