MySQL数据库基础命令
1.连接数据库在目录下输入cmd输入命令:mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -u root -p输入密码进入数据库2.显示系统所有数据库名称输入命令:show database;3.新建数据库oo命令:create database oo;建成后查看:4.使用数据库oo命令:use oo;5.在数据库oo中创建txt命令:create table txt(id int(8),name varc
1.连接数据库
在目录下输入cmd

输入命令:
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -u root -p
输入密码进入数据库


2.显示系统所有数据库名称
输入命令:
show database;

3.新建数据库oo
命令:
create database oo;
建成后查看:

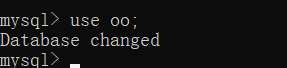
4.使用数据库oo
命令:
use oo;
5.在数据库oo中创建txt
命令:
create table txt(id int(8),name varchar(20),city varchar(20),score int(5));
![]()
6.在表txt中增加数据
在txt中插入如下5行数据;
命令:
Insert into txt(id,name,city,score) values(1,”wang”,”beijing”,75);
Insert into txt(id,name,city,score) values(3,”liu”,”shanghai”,80);
Insert into txt(id,name,city,score) values(5,”chen”,”fuzhou”,70);
Insert into txt(id,name,city,score) values(2,”zhou”,”xian”,90);
Insert into txt(id,name,city,score) values(7,”han”,”guangzhou”,65);

插入成功后,可铲鲟txt表中的全部内容;
命令:
select * from txt;

7.在表txt中删除一条数据
如果删除id=7的数据,其命令为:
delete from txt where id=7;
查看结果命令:
select * from txt;

8.修改表txt中的1条数据
如果修改id=5的数据,将其score设置为60,其命令:
update txt set score=60 where id=5;
修改成功后,查看命令:
select * from txt;

9.查询表txt中的数据
命令:
select * from txt;
查询表中所有字段

select name,score from txt;
查询表中的name和score字段

select score from txt where name=”wang”;
查询name为wang的学生的分数

order by 的用法
- 将result表中的数据按照分数(score)从高到低进行排序:
其中,desc表示递减;
asc 表示递增。

- 尝试命令:
select id,name,score from txt order by 1;
显示正常id排序结果。

select id,name,score from txt order by 2;
显示正常name升序排列。

select id,name,score from txt order by 3;
显示以score升序排列的结果。

select id,name,score from txt order by 4;
其为报错,

即可得到,命令:
select c1,c2,…,cn from txt order by M;
order by 后面的数字(M)必须小于或等于n(数据库查询的字段数),才能正常显示。如果M>n,数据库就会报错。
- limit的用法
基本格式:
limit M,N
表示从第M+1条数据开始,顺序往下查询N条数据
limit M
表示查询前M条数据
select * from txt limit 0,2;
查询表中前2条数据

select id,name,score from txt limit 1,3;
从第2条数据起,往下查询3条数据的id、name和score字段

- union select的用法
- select * from txt union select 1,2,3,4;
此语句的查询结果,即是select * from txt和select 1,2,3,,4查询结果的拼接。

- 尝试执行以下命令:
select id,name,score from txt union select 1,2,3;
正常显示!

select id,name,score from txt union select 1,2;
报错!
![]()
select id,name,score from txt union select 1,2,3,4;
报错!
![]()
从以上结果总结,可得:
select c1,c2…,cn from txt union select d1,d2,…dm;
后半句union select查询的字段数(m)必须与前半句select查询的字段数(n)相等,数据库才能正常显示结果。
- 命令:
select id,city from txt where id=1 and 1=2 union select name,score from txt;

- union select结合information_schema数据库
MySQL(MariaDB)5.5以上版本自带information_schema数据库,其中保存着MySQL服务器所维护的所有其他数据库的信息,可以把information_schema数据库看作MySQL的“目录”!
- 命令:
show databases;

select schema_name from information_schema.schemata;

两语句执行结果相同!
- 命令:
use oo;
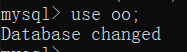
show tables;

select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=’oo’;
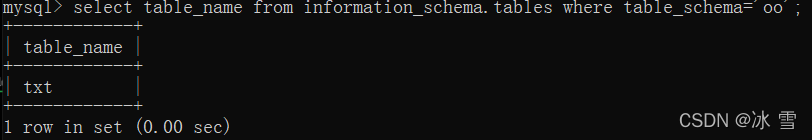
命令执行的结果相同!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)