Python正则表达式,看完这篇文章就够了...#华为云·寻找黑马程序员#
正则表达式简介正则表达式,是一个特殊的字符序列,又称规则表达式(英语:Regular Expression,在代码中常简写为regex、regexp 或RE),本质而言是一种小型的,高度专业化的编程语言。Python 自1.5版本起增加了re 模块,re 模块使Python语言拥有全部的正则表达式功能。正则语法表关于正则语法表,别想其他的都背过就行了。不管你是python还是其他...
正则表达式简介
正则表达式,是一个特殊的字符序列,又称规则表达式(英语:Regular Expression,在代码中常简写为regex、regexp 或RE),本质而言是一种小型的,高度专业化的编程语言。
Python 自1.5版本起增加了re 模块,re 模块使Python语言拥有全部的正则表达式功能。
正则语法表
关于正则语法表,别想其他的都背过就行了。不管你是python还是其他的语言都是一样的,所以背不过就抄到记住为止!这个你背不过,再好的教程看了也没用。如何巧记?我们需要对其进行分类。
-
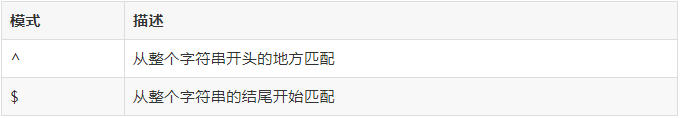
开头结尾
这一对标签,大家都不会陌生...
- 模糊匹配

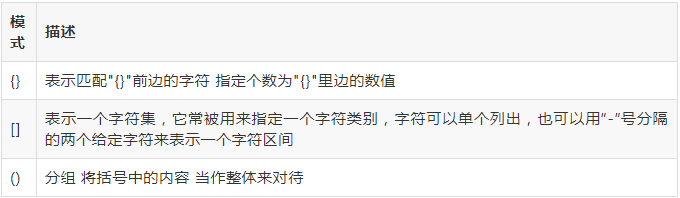
- 关于括号
- "\" 反斜杠的应用

- 其他

re模块用法
re.(function)(pattern[, flags])
pattern : 一个字符串形式的正则表达式
flags : 可选,表示匹配模式,比如忽略大小写,多行模式等,具体参数为:
-
re.I 忽略大小写
-
re.L 表示特殊字符集 \w, \W, \b, \B, \s, \S 依赖于当前环境
-
re.M 多行模式
-
re.S 即为 . 并且包括换行符在内的任意字符(. 不包括换行符)
-
re.U 表示特殊字符集 \w, \W, \b, \B, \d, \D, \s, \S 依赖于 Unicode 字符属性数据库
-
re.X 为了增加可读性,忽略空格和 # 后面的注释
-
findall() (即:全部找到,返回的是一个列表)
findall(string[, pos[, endpos]])
参数:
-
string : 待匹配的字符串。
-
pos : 可选参数,指定字符串的起始位置,默认为 0。
-
endpos : 可选参数,指定字符串的结束位置,默认为字符串的长度。
import re
s = 'helloworld hellobeijing'
ret = re.findall('hello\S+',s)
print(ret)
['helloworld', 'hellobeijing']-
finditer()
和 findall 类似,在字符串中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并把它们作为一个迭代器返回。
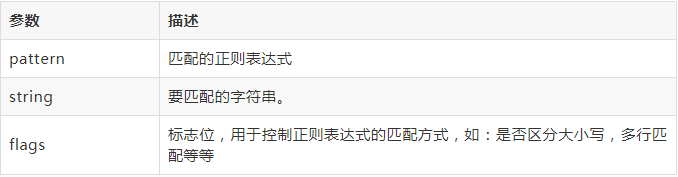
re.finditer(pattern, string, flags=0)
参数:
-
search() 与 match()
相同点:
-
语法:re.search/match(pattern, string, flags=0)
-
函数参数说明:
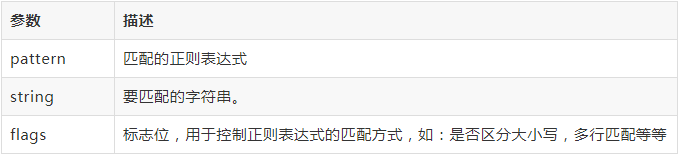
3.可以使用group(num) 或 groups() 匹配对象函数来获取匹配表达式。

import re
# re.search
ret = re.search('h..','hello hello world')
print(ret) # 输出结果:<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 3), match='hel'>
ret1 = re.search('h..','hello hello world').group()
print(ret1) # 输出结果:hel 只输出第一个符合条件的结果
# re.match
ret = re.match('asd','asdhskdjfksji')
print(ret) # 输出结果:<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 3), match='asd'>返回的是一个对象。
ret1 = re.match('asd','asdhskdjfasdksjiasd').group()
print(ret1) # 输出结果:asd 调用.group()方法,只返回匹配的第一个结果。不同点:
-
re.match只匹配字符串的开始,如果字符串开始不符合正则表达式,则匹配失败,函数返回None
-
re.search匹配整个字符串,直到找到一个匹配
# re.search
s = 'helloworld hellobeijing'
ret = re.search('hellob\S+',s)
print(ret)
<re.Match object; span=(11, 23), match='hellobeijing'>
# re.match
s = 'helloworld hellobeijing'
ret = re.match('hellob\S+',s)
print(ret)
None-
split() 分隔符 对比字符串里边的split方法。
split 方法按照能够匹配的子串将字符串分割后返回列表,它的使用形式如下:
re.split(pattern, string[, maxsplit=0, flags=0])

import re
s = 'helloworld hellobeijing'
ret = re.split('hello',s)
print(ret)
['', 'world ', 'beijing']-
sub() 替换;类似字符串中的replace()方法。
re.sub用于替换字符串中的匹配项。
语法:
re.sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0)
参数:
-
pattern : 正则中的模式字符串。
-
repl : 替换的字符串,也可为一个函数。
-
string : 要被查找替换的原始字符串。
-
count : 模式匹配后替换的最大次数,默认 0 表示替换所有的匹配。
import re
s = 'helloworld hellobeijing'
ret = re.sub('hello','goodbye',s)
print(ret)
goodbyeworld goodbyebeijing-
compile(strPattern[,flag]): 这个方法是Pattern类的工厂方法,用于将字符串形式的正则表达式编译为Pattern对象
compile 函数用于编译正则表达式,生成一个正则表达式( Pattern )对象,供 match() 和 search() 这两个函数使用。
语法格式为:
re.compile(pattern[, flags])
参数:
pattern : 一个字符串形式的正则表达式
-
flags : 可选,表示匹配模式,比如忽略大小写,多行模式等,具体参数为:
-
re.I 忽略大小写
-
re.L 表示特殊字符集 \w, \W, \b, \B, \s, \S 依赖于当前环境
-
re.M 多行模式
-
re.S 即为 . 并且包括换行符在内的任意字符(. 不包括换行符)
-
re.U 表示特殊字符集 \w, \W, \b, \B, \d, \D, \s, \S 依赖于 Unicode 字符属性数据库
-
re.X 为了增加可读性,忽略空格和 # 后面的注释
import re
pattern = re.compile('he.{3}')
pattern.match(s)
<re.Match object; span=(0, 5), match='hello'>The End
OK,今天的内容就到这里,如果觉得内容对你有所帮助,可以点击文章右下角的“在看”。
欢迎将这篇文章或我的微信公众号【清风Python】分享给更多喜欢python的人,谢谢。
作者:清风Python
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5412条内容
已为社区贡献5412条内容









所有评论(0)